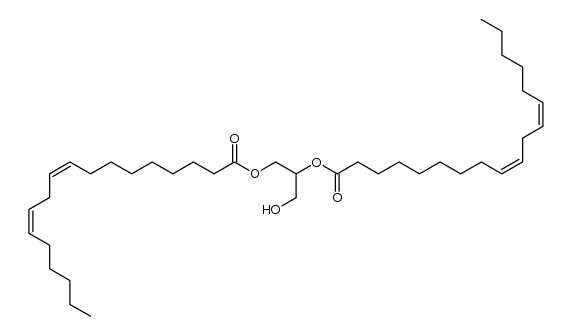
1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine

1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine structure
|
Common Name | 1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 998-06-1 | Molecular Weight | 782.08200 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C44H80NO8P | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of 1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholineL-Dilinoleoyllecithin is a phosphatidylcholine (PC or GPCho). It is a glycerophospholipid in which a phosphorylcholine moiety occupies a glycerol substitution site. As is the case with diacylglycerols, glycerophosphocholines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached at the C-1 and C-2 positions. Fatty acids containing 16, 18 and 20 carbons are the most common. PC(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)), in particular, consists of two chains of linoleic acid at the C-1 and C-2 positions. The linoleic acid moieties are derived from seed oils. Phospholipids, are ubiquitous in nature and are key components of the lipid bilayer of cells, as well as being involved in metabolism and signaling.While most phospholipids have a saturated fatty acid on C-1 and an unsaturated fatty acid on C-2 of the glycerol backbone, the fatty acid distribution at the C-1 and C-2 positions of glycerol within phospholipids is continually in flux, owing to phospholipid degradation and the continuous phospholipid remodeling that occurs while these molecules are in membranes. PCs can be synthesized via three different routes. In one route, choline is activated first by phosphorylation and then by coupling to CDP prior to attachment to phosphatidic acid. PCs can also synthesized by the addition of choline to CDP-activated 1,2-diacylglycerol. A third route to PC synthesis involves the conversion of either PS or PE to PC. |
| Name | 1,2-dilinoleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Molecular Formula | C44H80NO8P |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 782.08200 |
| Exact Mass | 781.56200 |
| PSA | 121.00000 |
| LogP | 12.34640 |
| InChIKey | FVXDQWZBHIXIEJ-LNDKUQBDSA-N |
| SMILES | CCCCCC=CCC=CCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(COP(=O)([O-])OCC[N+](C)(C)C)OC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CCC=CCCCCC |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
~% 
1,2-dilinoleoyl... CAS#:998-06-1 |
| Literature: Shveits,V.I. et al. J. Gen. Chem. USSR (Engl. Transl.), 1964 , vol. 34, p. 3983 - 3986,4042 - 4045 |
|
~%
Detail
|
| Literature: Shvets,V.I. et al. Chemistry of Natural Compounds, 1966 , vol. 2, p. 181 - 184 Khimiya Prirodnykh Soedinenii, 1966 , vol. 2, p. 225 - 229 |
|
Unsaturated lipids protect the integral membrane peptide gramicidin A from singlet oxygen
FEBS Lett. 588(9) , 1590-5, (2014) • Unsaturated lipids protect gramicidin channels from photosensitized inactivation. • Photosensitizer binding to membrane is independent of lipid unsaturation. • Double bonds in lipids reduce gramicid... |
|
|
Phase coexistence in films composed of DLPC and DPPC: A comparison between different model membrane systems
Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1838(7) , 1823-31, (2014) For the biophysical study of membranes, a variety of model systems have been used to measure the different parameters and to extract general principles concerning processes that may occur in cellular ... |
|
|
Optimization of the Electroformation of Giant Unilamellar Vesicles (GUVs) with Unsaturated Phospholipids.
J. Membr. Biol. 248 , 827-35, (2015) Giant unilamellar vesicles (GUV) are widely used cell membrane models. GUVs have a cell-like diameter and contain the same phospholipids that constitute cell membranes. The most frequently used protoc... |
| 1,2-DI9-CIS-12-CIS-OCTADECENOYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE |
| 1,2-DILINOLEOYL-SN-GLYCERO-3-PHOSPHOCHOLINE |
| Einecs 213-647-0 |
| 1,2-dilinoleic-glycerophosphatidylcholine |
| 1,2-dilinolenoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| 1,2-di-O-linoleoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylcholine |
| DILINOLEOYL LECITHIN |
| L-A-PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE DILINOLEOYL SYNTHETIC |
| L-A-PHOSPHATIDYLCHOLINE DILINOLEOYL,*LYO PHILIZED |