叔丁基硫醇
一般危化品
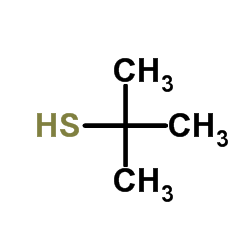
叔丁基硫醇结构式
|
常用名 | 叔丁基硫醇 | 英文名 | Tert-Butylthiol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 75-66-1 | 分子量 | 90.187 | |
| 密度 | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 67.0±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C4H10S | 熔点 | -1.1 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | -24.4±0.0 °C | |
| 符号 |



GHS02, GHS07, GHS09 |
信号词 | Danger |
叔丁基硫醇用途【用途一】 特丁硫醇是有机磷杀虫剂特丁硫磷的中间体。 |
| 中文名 | 2-甲基-2-丙硫醇 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | 2-Methyl-2-Propanethiol |
| 中文别名 | 叔丁基硫醇 | 叔丁硫醇 | 叔丁硫醇(TBM) | 第三丁硫醇 |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 密度 | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 67.0±8.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | -1.1 °C |
| 分子式 | C4H10S |
| 分子量 | 90.187 |
| 闪点 | -24.4±0.0 °C |
| 精确质量 | 90.050323 |
| PSA | 38.80000 |
| LogP | 1.95 |
| 外观性状 | 透明液体 |
| 蒸汽密度 | 3.1 (vs air) |
| 蒸汽压 | 160.1±0.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.437 |
| 储存条件 | 储存注意事项 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。库温不宜超过29℃。包装要求密封,不可与空气接触。应与氧化剂、酸类、碱金属等分开存放,切忌混储。采用防爆型照明、通风设施。禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。 |
| 稳定性 | 1.稳定性 稳定 2.禁配物 强氧化剂、酸类、酸酐、酰基氯、碱金属 3.避免接触的条件 受热 4.聚合危害 不聚合 5.分解产物 硫化氢 |
| 水溶解性 | 略溶于水 |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:28.44 2、 摩尔体积(cm3/mol):108.6 3、 等张比容(90.2K):238.2 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):23.1 5、 极化率(10-24cm3):11.27 |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):1.5 2.氢键供体数量:1 3.氢键受体数量:1 4.可旋转化学键数量:0 5.互变异构体数量:无 6.拓扑分子极性表面积1 7.重原子数量:5 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:25.1 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1.性状:无色液体,有不愉快气味。 2.熔点(℃):-0.5 3.沸点(℃):62~65 4.相对密度(水=1):0.80 5.相对蒸气密度(空气=1):3.1 6.饱和蒸气压(kPa):19.0(20℃) 7.临界压力(MPa):4.06 8.辛醇/水分配系数:2.14 9.闪点(℃):-26(CC) 10.溶解性:微溶于水,可混溶于乙醇、乙醚,溶于庚烷等。 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
叔丁基硫醇毒理学数据: 1.急性毒性 LD50:4729mg/kg(大鼠经口) LC50:22200ppm(大鼠吸入,4h);16500ppm(小鼠吸入,4h) 2.刺激性 家兔经眼84mg,引起刺激。 叔丁基硫醇生态学数据: 1.生态毒性 暂无资料 2.生物降解性 暂无资料 3.非生物降解性 暂无资料 4.其他有害作用 该物质对环境有危害,应特别注意对水体的污染。 |
| 符号 |



GHS02, GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Danger |
| 危害声明 | H225-H317-H411 |
| 警示性声明 | P210-P273-P280 |
| 个人防护装备 | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | F:Flammable;Xn:Harmful; |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | R11;R36;R43;R65 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S3-S16-S26-S39-S38-S36/37 |
| 危险品运输编码 | UN 2347 3/PG 2 |
| WGK德国 | 3 |
| RTECS号 | TZ7660000 |
| 包装等级 | II |
| 危险类别 | 3.1 |
由磺代叔丁烷与硫化锌在醇中反应而得。
|
Construction of RNA-Quantum Dot Chimera for Nanoscale Resistive Biomemory Application.
ACS Nano 9 , 6675-82, (2015) RNA nanotechnology offers advantages to construct thermally and chemically stable nanoparticles with well-defined shape and structure. Here we report the development of an RNA-QD (quantum dot) chimera... |
|
|
Stir fabric phase sorptive extraction for the determination of triazine herbicides in environmental waters by liquid chromatography.
J. Chromatogr. A. 1376 , 35-45, (2015) Stir fabric phase sorptive extraction (SFPSE), which integrates sol-gel hybrid organic-inorganic coated fabric phase sorptive extraction media with a magnetic stirring mechanism, is presented for the ... |
|
|
Formation and speciation of disinfection byproducts during chlor(am)ination of aquarium seawater.
J. Environ. Sci. (China) 33 , 116-24, (2015) The chemistry associated with the disinfection of aquarium seawater is more complicated than that of freshwater, therefore limited information is available on the formation and speciation of disinfect... |
| Tert-Butylthiol |
| 2-Methyl-2-propanethiol |
| t-Butyl mercaptan |
| TERT-BUTANETHIOL |
| tertiary-Butyl mercaptan |
| 2-Methylpropane-2-thiol |
| MFCD00004857 |
| t-Butylmercaptan |
| tert-butyl thiol |
| 1,1-Dimethylethanethiol |
| EINECS 200-890-2 |
| t-butylthiol |
| 2-Propanethiol, 2-methyl- |
| propane-2-thiol, 2-methyl- |
| tert.-Butanethiol |
| tert-Butyl Mercaptan |
| tert-Butylmercaptan |
