| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
甘油
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
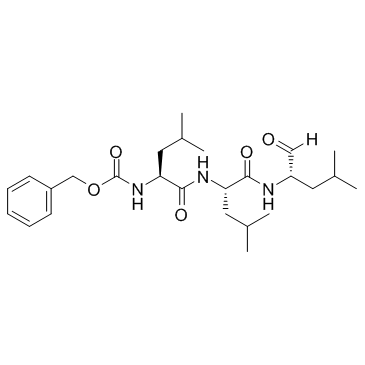 |
蛋白酶体抑制剂
CAS:133407-82-6 |
|
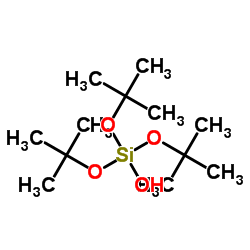 |
三(叔丁氧基)硅烷醇
CAS:18166-43-3 |
|
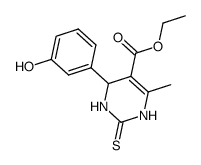 |
莫纳托
CAS:254753-54-3 |
|
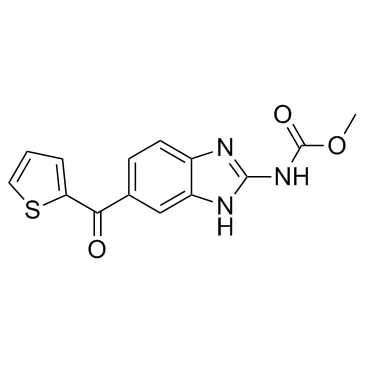 |
诺考达唑
CAS:31430-18-9 |