核苷酸
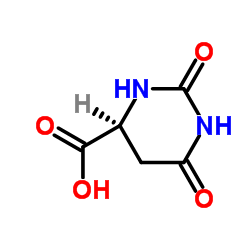
核苷酸结构式

|
常用名 | 核苷酸 | 英文名 | L-Dihydroorotic acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 5988-19-2 | 分子量 | 158.112 | |
| 密度 | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 524.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C5H6N2O4 | 熔点 | 254-255 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 270.7±32.9 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
核苷酸用途【用途一】 用作增鲜剂、调味剂,可用于家庭、餐饮业等 |
| 中文名 | 核苷酸 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | (S)-dihydroorotic acid |
| 中文别名 | 鸟苷磷酸二钠盐(GMP) | 腺苷-5-磷酸(AMP) | L-氢化乳清酸 | L-4,5-二氢乳清酸 | 核糖核酸(酵母)RNA |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | L-Dihydroorotic acid 可通过二氢乳清酶可逆水解产生无环的 L-脲基琥珀酸。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 靶点实验 |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 524.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 254-255 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| 分子式 | C5H6N2O4 |
| 分子量 | 158.112 |
| 闪点 | 270.7±32.9 °C |
| 精确质量 | 158.032761 |
| PSA | 95.50000 |
| LogP | -2.29 |
| InChIKey | UFIVEPVSAGBUSI-REOHCLBHSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C1CC(C(=O)O)NC(=O)N1 |
| 外观性状 | 白色至灰白色结晶粉末 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.714 |
| 储存条件 | 0-5℃ 避光,阴凉干燥处,密封保存 |
| 稳定性 | 常温常压下稳定,结晶。系生物嘧啶如胸腺嘧啶、尿嘧啶、胞嘧啶、羟甲基胞嘧啶的前体。266℃分解。比旋光度[α]D25.3 +33.23°(C=1.992,1%碳酸氢钠溶液中)。有刺激性。 |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:31.51 2、 摩尔体积(m3/mol):103.7 3、 等张比容(90.2K):287.6 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):59.0 5、 极化率(10 -24cm 3):12.49 |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):-1.5 2.氢键供体数量:3 3.氢键受体数量:4 4.可旋转化学键数量:1 5.互变异构体数量:8 6.拓扑分子极性表面积95.5 7.重原子数量:11 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:225 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:1 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:未确定 2. 密度(g/mL,25/4℃):未确定 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):未确定 4. 熔点(ºC):254-255 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):未确定 6. 沸点(ºC,5.2kPa):未确定 7. 折射率:未确定 8. 闪点(ºC):未确定 9. 比旋光度(º):未确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):未确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC):未确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):未确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):未确定 14. 临界温度(ºC):未确定 15. 临界压力(KPa):未确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:未确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):未确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):未确定 19. 溶解性:未确定 |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| 信号词 | Warning |
| 危害声明 | H315-H319-H335 |
| 警示性声明 | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| 个人防护装备 | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| 危害码 (欧洲) | Xi:Irritant |
| 风险声明 (欧洲) | R36/37/38 |
| 安全声明 (欧洲) | S26-S36 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK德国 | 3 |
| 海关编码 | 2934999001 |
| 海关编码 | 2934999001 |
|---|
|
SEC-TID: A Label-Free Method for Small-Molecule Target Identification.
J. Biomol. Screen. 19(6) , 917-927, (2014) Bioactive small molecules are an invaluable source of therapeutics and chemical probes for exploring biological pathways. Yet, significant hurdles in drug discovery often come from lacking a comprehen... |
|
|
The structures of human dihydroorotate dehydrogenase with and without inhibitor reveal conformational flexibility in the inhibitor and substrate binding sites.
Biochemistry 47(34) , 8929-36, (2008) Inhibitors of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) have been suggested for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, autoimmune diseases, Plasmodium, and bacterial and fungal infections. Here ... |
|
|
Miller (Genee-Wiedemann) syndrome represents a clinically and biochemically distinct subgroup of postaxial acrofacial dysostosis associated with partial deficiency of DHODH.
Hum. Mol. Genet. 21(18) , 3969-83, (2012) Biallelic mutations in the gene encoding DHOdehase [dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH)], an enzyme required for de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis, have been identified as the cause of Miller (Genée-We... |
|
实验名称:Experimentally measured binding affinity data (Kd) for protein-ligand complexes deriv...
来源:Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry
靶标:N/A
External Id:PDBbind-Kd for protein-ligand complexes
|
| (S)-dihydroorotic acid |
| dihydroorotate |
| MFCD00085339 |
| (S)-2,6-Dioxohexahydro-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid |
| (S)-2,6-dioxo-hexahydro-pyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid |
| (4S)-2,6-Dioxohexahydropyrimidine-4-carboxylic acid |
| (4S)-2,6-Dihydroxy-4,5-dihydro-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid |
| L-Dihydroorotic Acid |
| (4S)-2,6-Dioxohexahydro-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid |
| EINECS 204-352-8 |

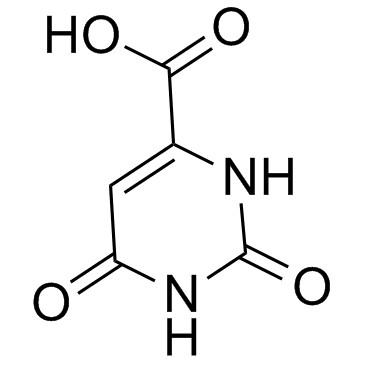 CAS号65-86-1
CAS号65-86-1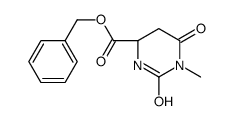 CAS号103300-85-2
CAS号103300-85-2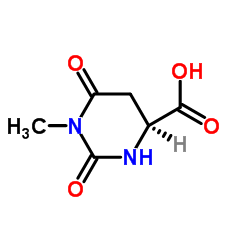 CAS号103365-69-1
CAS号103365-69-1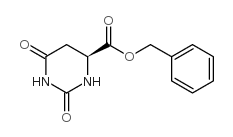 CAS号103300-84-1
CAS号103300-84-1





