| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
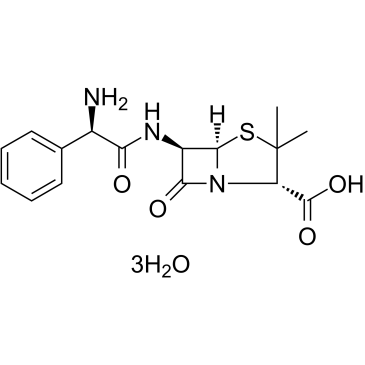 |
Ampicillin Trihydrate
CAS:7177-48-2 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
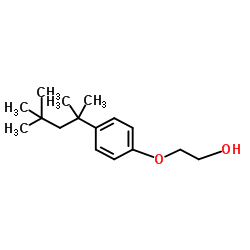 |
2-(4-(1,1,3,3-Tetramethylbutyl)phenoxy)ethanol
CAS:2315-67-5 |
|
 |
Ampicillin
CAS:69-53-4 |
|
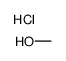 |
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE ~1.25 M IN METHANOL, 250 ML
CAS:132228-87-6 |