| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
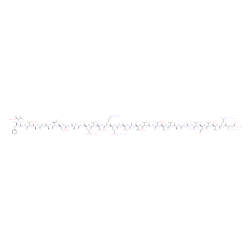 |
α-Synuclein (61-95) (human) trifluoroacetate salt
CAS:154040-19-4 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
Calcium chloride
CAS:10043-52-4 |
|
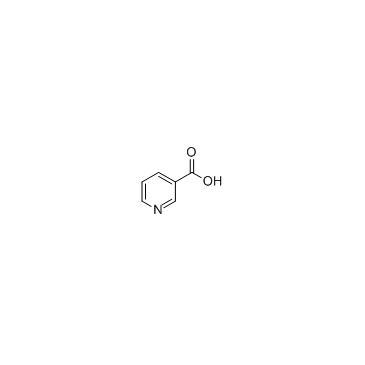 |
Nicotinic acid
CAS:59-67-6 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
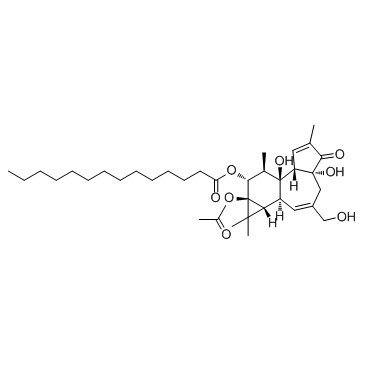 |
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
CAS:16561-29-8 |
|
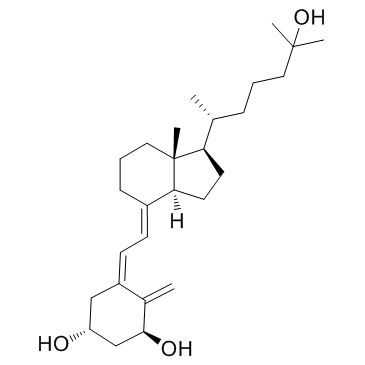 |
Calcitriol
CAS:32222-06-3 |
|
 |
Endoproteinase Arg-C
CAS:82047-85-6 |