| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
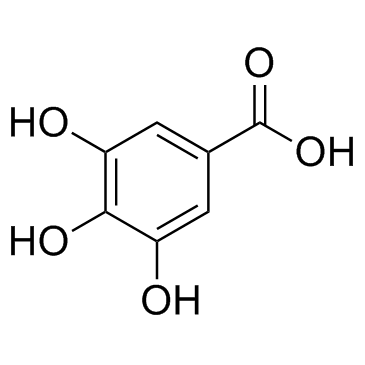 |
Gallic acid
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
 |
D-(+)-Glucose
CAS:50-99-7 |
|
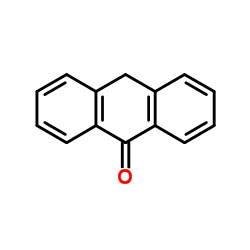 |
Anthrone
CAS:90-44-8 |
|
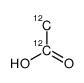 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
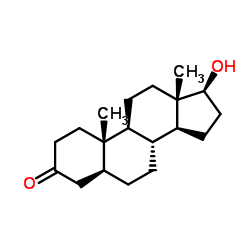 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |