| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium Fluoride
CAS:7681-49-4 |
|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
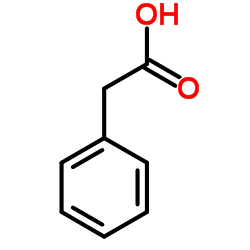 |
Phenylacetic acid
CAS:103-82-2 |
|
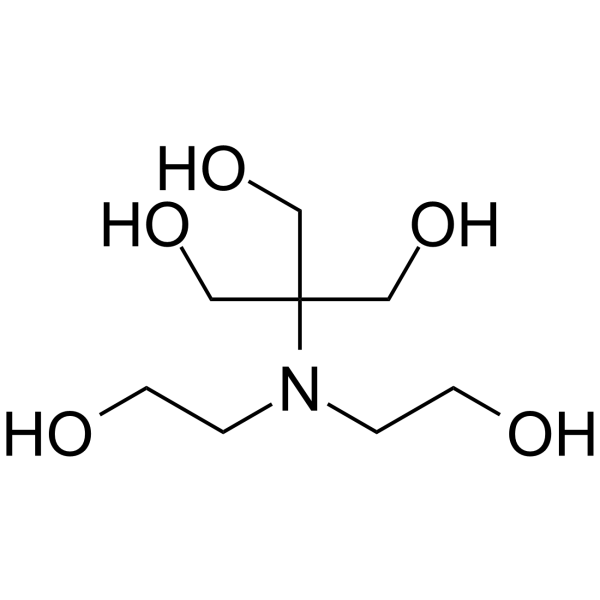 |
Bis-tris methane
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
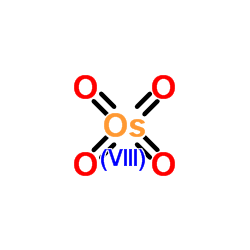 |
Osmium tetroxide
CAS:20816-12-0 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
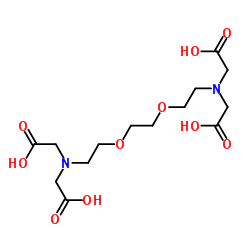 |
EGTA
CAS:67-42-5 |
|
 |
bisphenol A diglycidyl ether
CAS:1675-54-3 |
|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |