EGTA
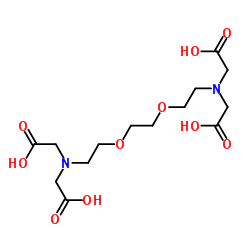
EGTA structure
|
Common Name | EGTA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 67-42-5 | Molecular Weight | 380.348 | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 678.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H24N2O10 | Melting Point | 241 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 363.9±31.5 °C | |
Use of EGTAEGTA is a specific calcium ion chelator. EGTA has an apparent calcium dissociation constant (Kd) of 60.5 nM at physiological pH (7.4) and has very high specificity for Ca2+ over Mg2+ (Mg2+ Kd 1-10 mM). EGTA significantly inhibited the substrate adherence capacity of inflammatory macrophages[1][2]. |
| Name | ethylene glycol bis(2-aminoethyl)tetraacetic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | EGTA is a specific calcium ion chelator. EGTA has an apparent calcium dissociation constant (Kd) of 60.5 nM at physiological pH (7.4) and has very high specificity for Ca2+ over Mg2+ (Mg2+ Kd 1-10 mM). EGTA significantly inhibited the substrate adherence capacity of inflammatory macrophages[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | EGTA, proposed as endodontic irrigant, decreases substrate adherence capacity of inflammatory macrophages in a time- and dose-dependent manner. The EGTA concentration that causes an IC50 is 202 mM. Chelators react with calcium ions in the hydroxyapatite crystals to produce a metallic chelate. Removal of calcium ions from the dentine makes the dentinal tissue softer, especially the hydroxyapatite-rich peritubular dentin and increases the diameter of exposed dentinal tubules[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 678.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 241 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C14H24N2O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 380.348 |
| Flash Point | 363.9±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 380.143097 |
| PSA | 174.14000 |
| LogP | -2.53 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±4.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.547 |
| InChIKey | DEFVIWRASFVYLL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CN(CCOCCOCCN(CC(=O)O)CC(=O)O)CC(=O)O |
| Storage condition | Store at RT. |
| Water Solubility | slightly soluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
~% 
EGTA CAS#:67-42-5 |
| Literature: US2709178 , ; |
| Precursor 2 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| HS Code | 29225000 |
|---|
|
Functional consequence of the MET-T1010I polymorphism in breast cancer.
Oncotarget 6(5) , 2604-14, (2015) Major breast cancer predisposition genes, only account for approximately 30% of high-risk breast cancer families and only explain 15% of breast cancer familial relative risk. The HGF growth factor rec... |
|
|
Immunomodulation by the Pseudomonas syringae HopZ type III effector family in Arabidopsis.
PLoS ONE 9(12) , e116152, (2014) Pseudomonas syringae employs a type III secretion system to inject 20-30 different type III effector (T3SE) proteins into plant host cells. A major role of T3SEs is to suppress plant immune responses ... |
|
|
Targeting glucose uptake with siRNA-based nanomedicine for cancer therapy.
Biomaterials 51 , 1-11, (2015) Targeting cancer metabolism is emerging as a successful strategy for cancer therapy. However, most of the marketed anti-metabolism drugs in cancer therapy do not distinguish normal cells from cancer c... |
| Egtazic acid |
| ethylene glycol bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid |
| Egtazic |
| 4F 4PP oxalate |
| CHEL-DE |
| Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid |
| EGTA |
| AEGT |
| ethylene glycol bis(2-aminoethyl)tetraacetic acid |
| (Ethylenebis(oxyethylenenitrilo))tetraacetic acid |
| Ethylene glycol bis(2-aminoethyl ether)tetraacetic acid |
| EINECS 200-651-2 |
| Ethylene glycol-bis(2-aminoethylether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid |
| Ethylenebis(oxyethylenenitrilo)tetraacetic acid |
| MFCD00004291 |
| 3,12-Bis(carboxymethyl)-6,9-dioxa-3,12-diazatetradecane-1,14-dioic acid |
| chel tm-de |
| GIETA |
| [ethylenebis(oxyethylenenitrilo)]tetraacetic acid |
| 6,9-Dioxa-3,12-diazatetradecanedioic acid, 3,12-bis(carboxymethyl)- |
| GEDTA |
| ebonta |
| 3,6-dioxaoctamethylenedinitrilotetraacetic acid |