L-Glutamine

L-Glutamine structure
|
Common Name | L-Glutamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 56-85-9 | Molecular Weight | 146.145 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 353.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10N2O3 | Melting Point | 185ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 167.6±30.7 °C | |
Use of L-GlutamineL-Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid present abundantly throughout the body and is involved in gastrointestinal disorders.Target: mGluRGlutamine (abbreviated as Gln or Q) is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the standard genetic code. It is not recognized as an essential amino acid, but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders. Its side-chain is an amide formed by replacing the side-chain hydroxyl of glutamic acid with an amine functional group, making it the amide of glutamic acid. Its codons are CAA and CAG. In human blood, glutamine is the most abundant free amino acid, with a concentration of about 500-900 μmol/L. Glutamine is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia. The most relevant glutamine-producing tissue is the muscle mass, accounting for about 90% of all glutamine synthesized. Glutamine is also released, in small amounts, by the lung and the brain. Although the liver is capable of relevant glutamine synthesis, its role in glutamine metabolism is more regulatory than producing, since the liver takes up large amounts of glutamine derived from the gut. The most eager consumers of glutamine are the cells of intestines, the kidney cells for the acid-base balance, activated immune cells, and manycancer cells. In respect to the last point mentioned, different glutamine analogues, such as DON, Azaserine or Acivicin, are tested as anticancer drugs. |
| Name | L-glutamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | L-Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid present abundantly throughout the body and is involved in gastrointestinal disorders.Target: mGluRGlutamine (abbreviated as Gln or Q) is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the standard genetic code. It is not recognized as an essential amino acid, but may become conditionally essential in certain situations, including intensive athletic training or certain gastrointestinal disorders. Its side-chain is an amide formed by replacing the side-chain hydroxyl of glutamic acid with an amine functional group, making it the amide of glutamic acid. Its codons are CAA and CAG. In human blood, glutamine is the most abundant free amino acid, with a concentration of about 500-900 μmol/L. Glutamine is synthesized by the enzyme glutamine synthetase from glutamate and ammonia. The most relevant glutamine-producing tissue is the muscle mass, accounting for about 90% of all glutamine synthesized. Glutamine is also released, in small amounts, by the lung and the brain. Although the liver is capable of relevant glutamine synthesis, its role in glutamine metabolism is more regulatory than producing, since the liver takes up large amounts of glutamine derived from the gut. The most eager consumers of glutamine are the cells of intestines, the kidney cells for the acid-base balance, activated immune cells, and manycancer cells. In respect to the last point mentioned, different glutamine analogues, such as DON, Azaserine or Acivicin, are tested as anticancer drugs. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 353.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 185ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 146.145 |
| Flash Point | 167.6±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 146.069138 |
| PSA | 106.41000 |
| LogP | -1.28 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.564 |
| InChIKey | ZDXPYRJPNDTMRX-VKHMYHEASA-N |
| SMILES | NC(=O)CCC(N)C(=O)O |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
ZEB2 drives immature T-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia development via enhanced tumour-initiating potential and IL-7 receptor signalling.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 5794, (2015) Early T-cell precursor leukaemia (ETP-ALL) is a high-risk subtype of human leukaemia that is poorly understood at the molecular level. Here we report translocations targeting the zinc finger E-box-bin... |
|
|
Targeting glucose uptake with siRNA-based nanomedicine for cancer therapy.
Biomaterials 51 , 1-11, (2015) Targeting cancer metabolism is emerging as a successful strategy for cancer therapy. However, most of the marketed anti-metabolism drugs in cancer therapy do not distinguish normal cells from cancer c... |
|
|
25-O-acetyl-23,24-dihydro-cucurbitacin F induces cell cycle G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human soft tissue sarcoma cells.
J. Ethnopharmacol. 164 , 265-72, (2015) Quisqualis indica is used in traditional Chinese medicine to treat cancer and related syndromes and also known for its anthelminthic effects.Soft tissue sarcomas represent a rare group of malignant tu... |
| UNII-U5JDO2770Z |
| EINECS 200-292-1 |
| (2S)-2-((2S)-2-Aminopropanoylamino)-4-carbamoylbutanoic acid |
| ZY1&VMYVQ2VZ &&L-L Form |
| glutaminic acid |
| Gln |
| L-Ala-L-Gln |
| glutamine |
| L-Gln |
| L-Alanyl-L-glutamine |
| Levoglutamide |
| (S)-5-Amino-2-[(S)-2-aminopropanamido]-5-oxopentanoic acid |
| L-Glutamine,L-alanyl |
| (2S)-2-amino-4-carbamoylbutanoic acid |
| Alanyl-glutamine,Glutamine-S |
| MFCD00008044 |
| Ala-Gln |
| L-(+)-Glutamine |
| (S)-(+)-Glutamine |
| 5-Hydroxy-5-imino-L-norvaline |
| N(2)-L-alanyl-L-glutamine |
| Glutamine-S |
| Alanyl-glutamine |
| L-Glutamic Acid g-Amide |
| L-Glutamic acid γ-amide |
| N-L-alanyl-L-glutamine |
| L-Glutamine |
| l-alanyl-l-glutamin |
| l-(+)-glutamic acid-5-amide |
| L-Glutamic acid 5-amide |
| H-Ala-Gln-OH |
| (2S)-5-Amino-2-{[(2S)-2-aminopropanoyl]amino}-5-oxopentanoic acid |
| S(+)-Glutamic acid 5-amide |
| H-Gln-OH |
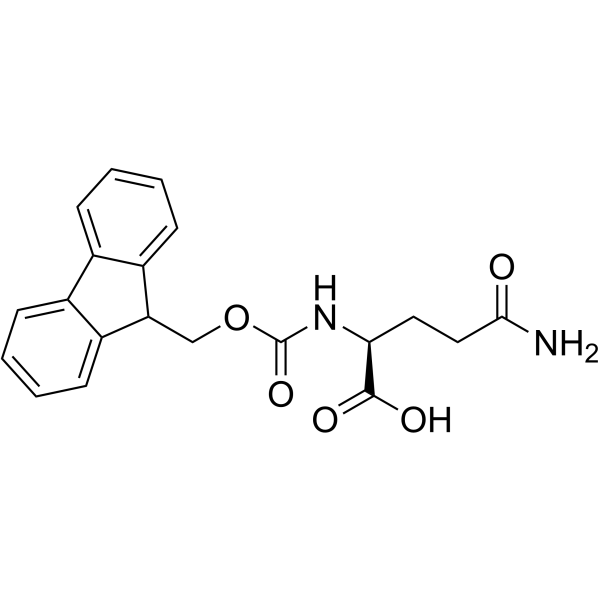 CAS#:71989-20-3
CAS#:71989-20-3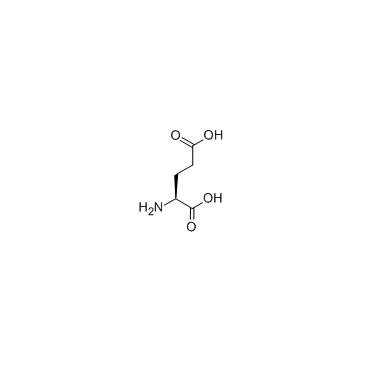 CAS#:56-86-0
CAS#:56-86-0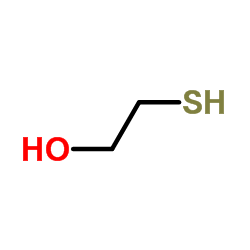 CAS#:60-24-2
CAS#:60-24-2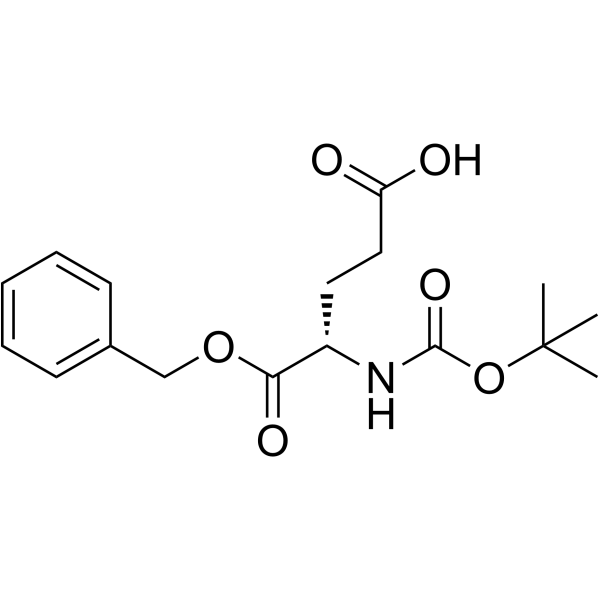 CAS#:30924-93-7
CAS#:30924-93-7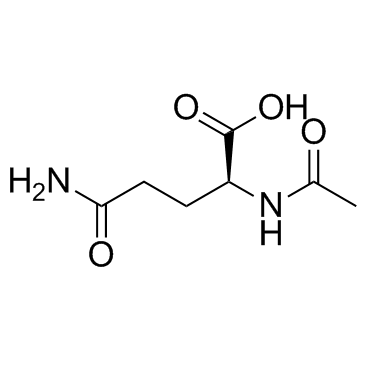 CAS#:2490-97-3
CAS#:2490-97-3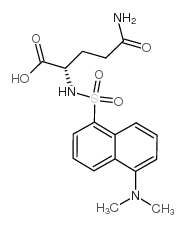 CAS#:1101-67-3
CAS#:1101-67-3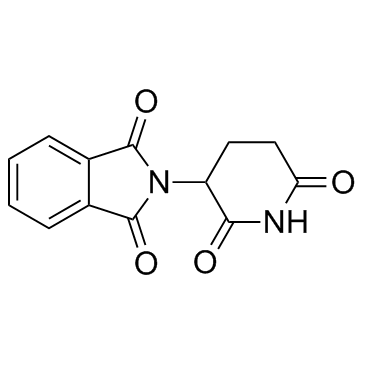 CAS#:50-35-1
CAS#:50-35-1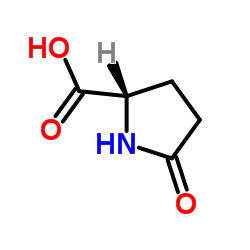 CAS#:149-87-1
CAS#:149-87-1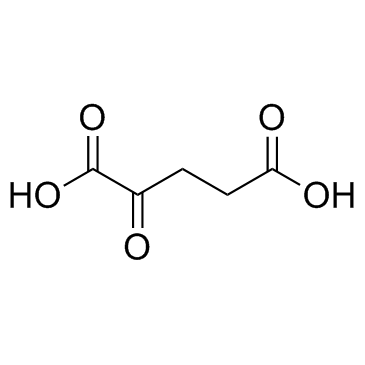 CAS#:328-50-7
CAS#:328-50-7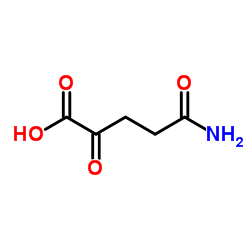 CAS#:18465-19-5
CAS#:18465-19-5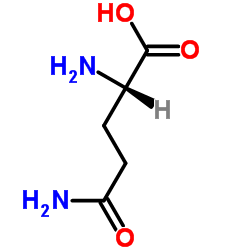 CAS#:39537-23-0
CAS#:39537-23-0 CAS#:3081-61-6
CAS#:3081-61-6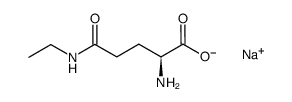 CAS#:945623-40-5
CAS#:945623-40-5 CAS#:3343-29-1
CAS#:3343-29-1
