| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethidium bromide
CAS:1239-45-8 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
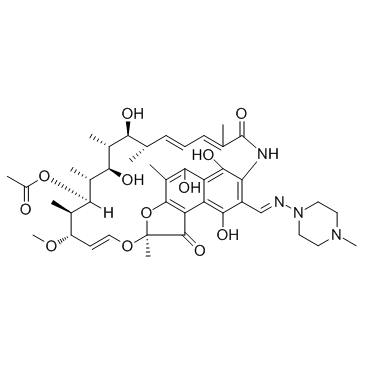 |
Rifampicin
CAS:13292-46-1 |
|
 |
Erythromycin
CAS:114-07-8 |
|
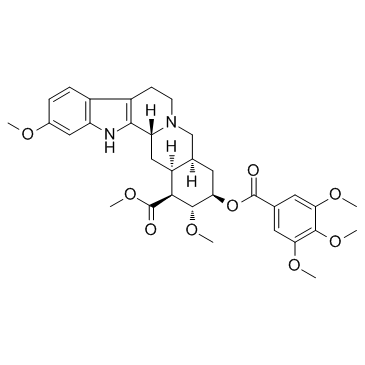 |
Reserpine
CAS:50-55-5 |
|
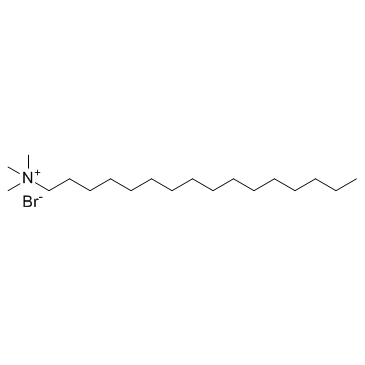 |
Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
CAS:57-09-0 |
|
 |
Trimethoprim
CAS:738-70-5 |
|
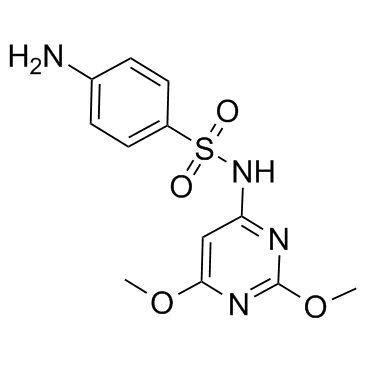 |
Sulfadimethoxine
CAS:122-11-2 |
|
 |
CCCP
CAS:555-60-2 |