| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
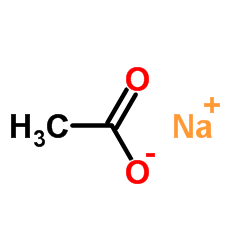 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
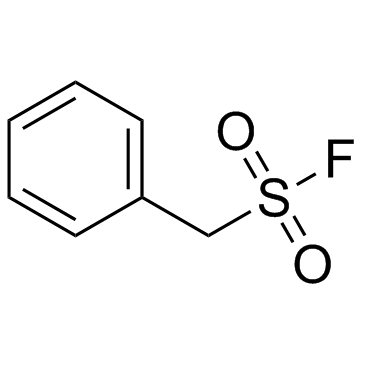 |
PMSF
CAS:329-98-6 |
|
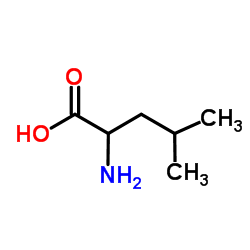 |
2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
CAS:328-39-2 |