| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
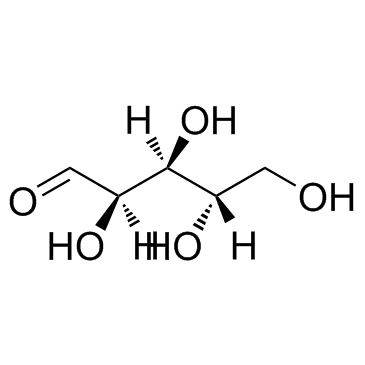 |
L-(+)-Arabinose
CAS:5328-37-0 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
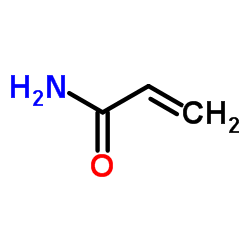 |
Acrylamide Crystals
CAS:79-06-1 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |