| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
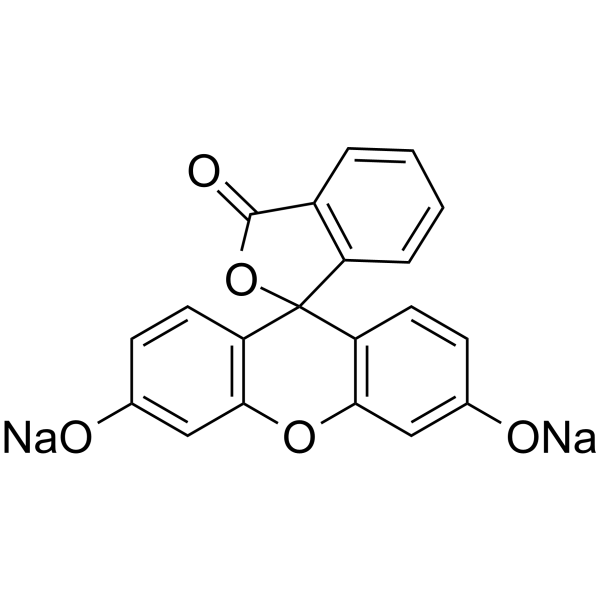 |
Fluorescein sodium
CAS:518-47-8 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
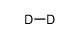 |
deuterium
CAS:7782-39-0 |
|
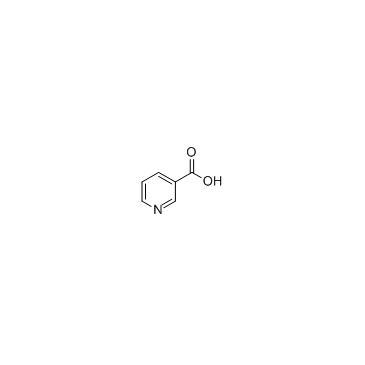 |
Nicotinic acid
CAS:59-67-6 |
|
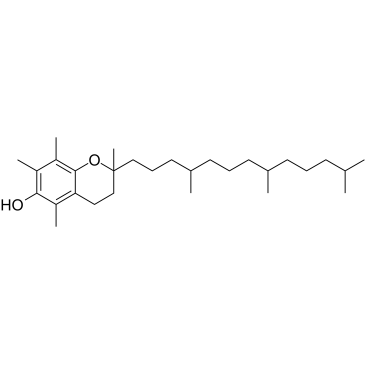 |
Vitamin E
CAS:10191-41-0 |
|
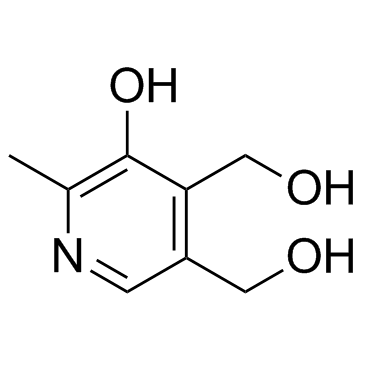 |
Pyridoxine
CAS:65-23-6 |
|
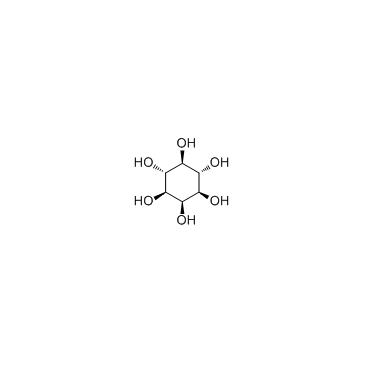 |
Inositol
CAS:87-89-8 |
|
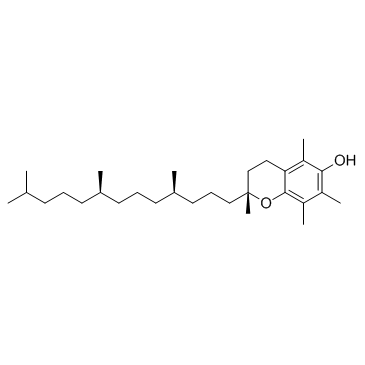 |
DL-alpha-Tocopherol
CAS:59-02-9 |