| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
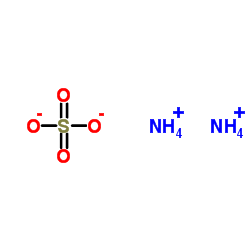 |
ammonium sulphate
CAS:7783-20-2 |
|
 |
sodium dihydrogenphosphate
CAS:7558-80-7 |
|
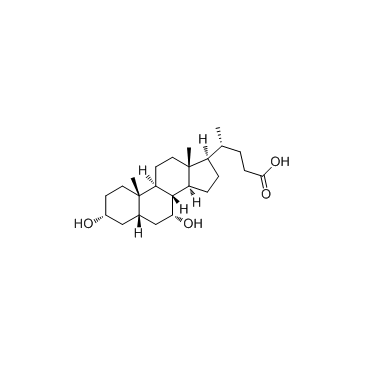 |
Chenodeoxycholic acid
CAS:474-25-9 |
|
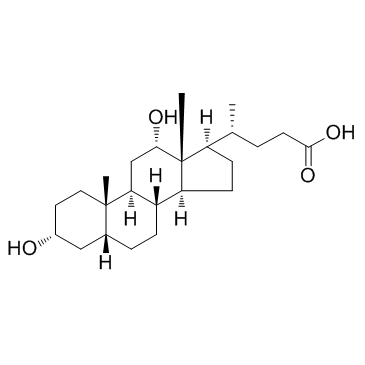 |
Deoxycholic acid
CAS:83-44-3 |
|
 |
Sodium deoxycholate
CAS:302-95-4 |
|
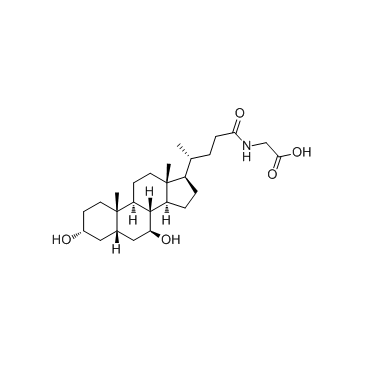 |
Glycoursodeoxycholic acid
CAS:64480-66-6 |
|
 |
cholic acid
CAS:81-25-4 |