| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
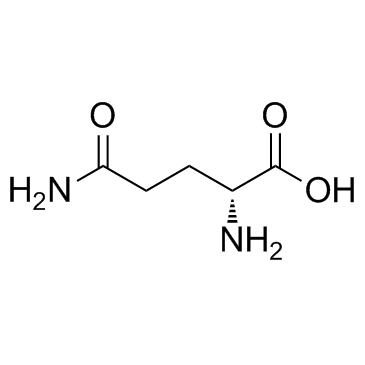 |
D-glutamine
CAS:5959-95-5 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |