D-glutamine
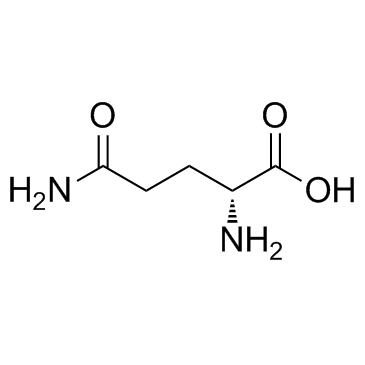
D-glutamine structure
|
Common Name | D-glutamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 5959-95-5 | Molecular Weight | 146.145 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 353.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10N2O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 167.6±30.7 °C | |
Use of D-glutamineD-Glutamine is a cell-permeable D type stereoisomer of Glutamine. |
| Name | D-glutamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | D-Glutamine is a cell-permeable D type stereoisomer of Glutamine. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Glutamine is a key amino acid in the central nervous system (CNS), playing an important role in the glutamate/GABA-Glutamine cycle (GGC). In the GGC,Glutamine is transferred from astrocytes to neurons, where it will replenish the inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmitter pools[1]. D-Glutamine has been used to study its role in conferring protection against acetaldehyde-induced disruption of barrier function in Caco-2 cell monolayer. Role of L-Glutamine in the protection of intestinal epithelium from acetaldehyde-induced disruption of barrier function is evaluated in Caco-2 cell monolayer. L-Glutamine reduced the acetaldehyde-induced decrease in transepithelilal electrical resistance and increase in permeability to inulin and lipopolysaccharide in a time- and dose-dependent manner; D-Glutamine, L-aspargine, L-arginine, L-lysine, or L-alanine produced no significant protection. D-Glutamine also fails to influence the acetaldehyde-induced decrease in TER and increase in inulin flux. D-Glutamine or glutaminase inhibitor by themselves did not influence TER or inulin flux in control or acetaldehyde-treated cell monolayers. Lack of effect of D-Glutamine in protection from acetaldehyde indicates that the L-Glutamine-mediated protection is stereospecific[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Effect of D-Glutamine and glutaminase inhibitor on acetaldehyde-induced permeability. Caco-2 cell monolayers are incubated for 4 h without or with acetaldehyde (600 μM) and L-Glutamine or D-Glutamine (2 mM) in the absence or presence of 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine (DON). Transepithelial electrical resistance (TER) and FITC-inulin flux are measured. Values are means±SE (n=6)[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 353.5±52.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 146.145 |
| Flash Point | 167.6±30.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 146.069138 |
| PSA | 106.41000 |
| LogP | -1.28 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.564 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| HS Code | 29241900 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 2 | |
| HS Code | 2924199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2924199090. other acyclic amides (including acyclic carbamates) and their derivatives; salts thereof. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |
|
Endogenous VEGF is required for visual function: evidence for a survival role on müller cells and photoreceptors.
PLoS ONE 3(11) , e3554, (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is well known for its role in normal and pathologic neovascularization. However, a growing body of evidence indicates that VEGF also acts on non-vascular cell... |
|
|
Müller and macrophage-like cell interactions in an organotypic culture of porcine neuroretina.
Mol. Vis. 14 , 2148-56, (2008) To analyze the in vitro Müller cell modifications in an organotypic culture of porcine neuroretina in response to the addition of a blood-derived mononuclear fraction (MNF; monocytes and lymphocytes) ... |
|
|
Ectodermal-neural cortex 1 down-regulates Nrf2 at the translational level.
PLoS ONE 4(5) , e5492, (2009) The transcription factor Nrf2 is the master regulator of a cellular defense mechanism against environmental insults. The Nrf2-mediated antioxidant response is accomplished by the transcription of a ba... |
| UNII-U5JDO2770Z |
| D-2-Aminoglutaramic acid |
| (2S)-2-((2S)-2-Aminopropanoylamino)-4-carbamoylbutanoic acid |
| ZY1&VMYVQ2VZ &&L-L Form |
| glutaminic acid |
| D-Glutamic acid 5-amide |
| Gln |
| L-Ala-L-Gln |
| glutamine |
| L-Gln |
| Pentanoic acid, 2,5-diamino-5-oxo-, (S)- |
| L-Alanyl-L-glutamine |
| Levoglutamide |
| (S)-5-Amino-2-[(S)-2-aminopropanamido]-5-oxopentanoic acid |
| MFCD00065607 |
| L-Glutamine,L-alanyl |
| 2,5-Diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid, (S)- |
| (2S)-2-amino-4-carbamoylbutanoic acid |
| Alanyl-glutamine,Glutamine-S |
| (2R)-2,5-diamino-5-oxopentanoic acid |
| Ala-Gln |
| L-(+)-Glutamine |
| 2-Aminoglutaramic acid, L- |
| (S)-(+)-Glutamine |
| 5-Hydroxy-5-imino-L-norvaline |
| 2-amino-4-carbamoylbutanoic acid |
| N(2)-L-alanyl-L-glutamine |
| Glutamine-S |
| Alanyl-glutamine |
| L-Norvaline, 5-hydroxy-5-imino- |
| L-Glutamic Acid g-Amide |
| H-D-Gln-OH |
| L-Glutamic acid γ-amide |
| N-L-alanyl-L-glutamine |
| L-Glutamine, N2-L-alanyl- |
| L-Glutamine |
| l-alanyl-l-glutamin |
| l-(+)-glutamic acid-5-amide |
| L-Glutamic acid 5-amide |
| H-Ala-Gln-OH |
| GLUTAMINE, L- |
| (2S)-5-Amino-2-{[(2S)-2-aminopropanoyl]amino}-5-oxopentanoic acid |
| L-Glutamine, L-alanyl- |
| S(+)-Glutamic acid 5-amide |
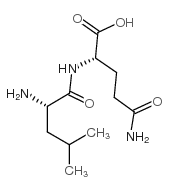 CAS#:38062-69-0
CAS#:38062-69-0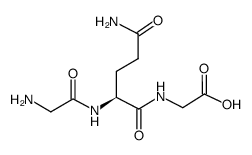 CAS#:2650-69-3
CAS#:2650-69-3
