| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
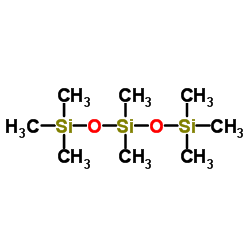 |
Octamethyltrisiloxane
CAS:107-51-7 |
|
 |
Hexamethyldisiloxane
CAS:107-46-0 |
|
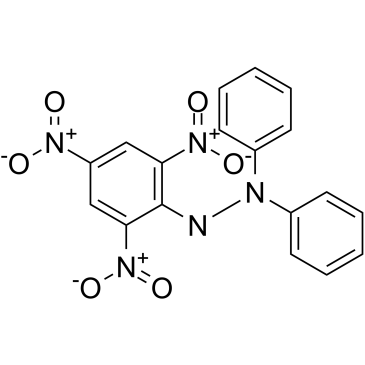 |
DPPH
CAS:1898-66-4 |
|
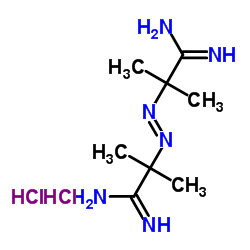 |
2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionamidine) dihydrochloride
CAS:2997-92-4 |
|
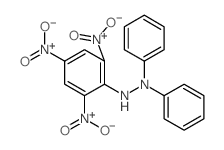 |
1,1-DIPHENYL-2-PICRYLHYDRAZINE
CAS:1707-75-1 |