| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
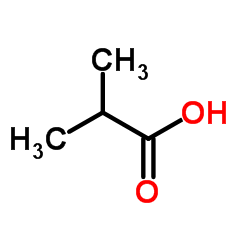 |
Isobutyric acid
CAS:79-31-2 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
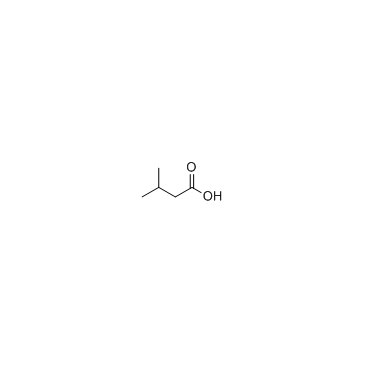 |
3-Methylbutanoic acid
CAS:503-74-2 |
|
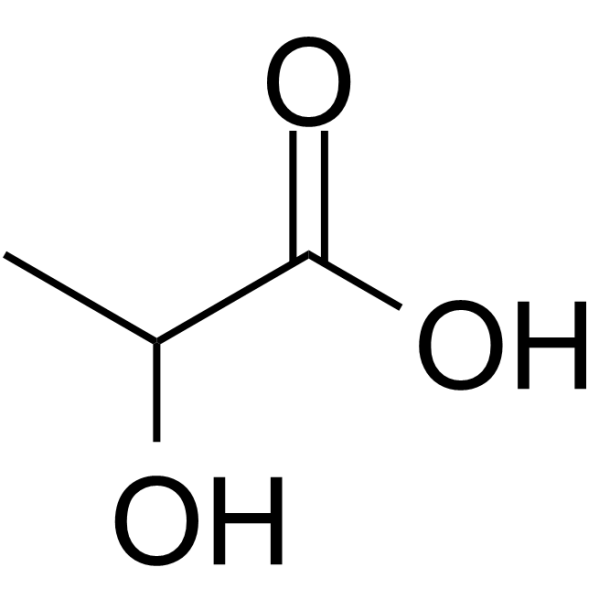 |
Lactic acid
CAS:50-21-5 |
|
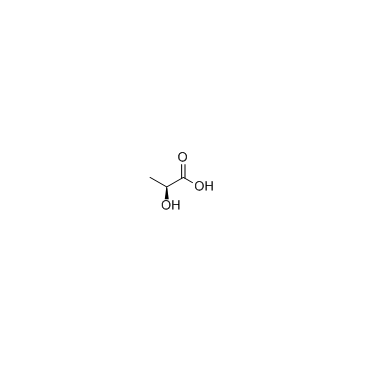 |
L-Lactic acid
CAS:79-33-4 |
|
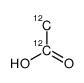 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
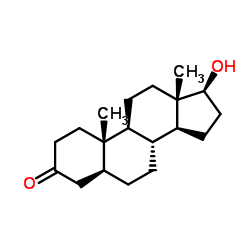 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
 |
Indole-3-butyric acid potassium salt
CAS:60096-23-3 |