| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
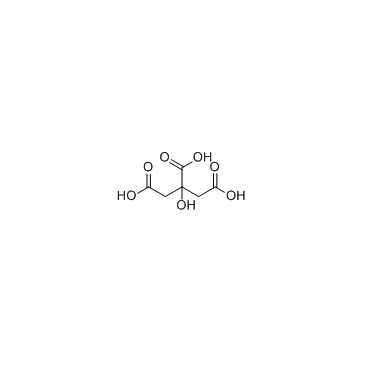 |
Citric Acid
CAS:77-92-9 |
|
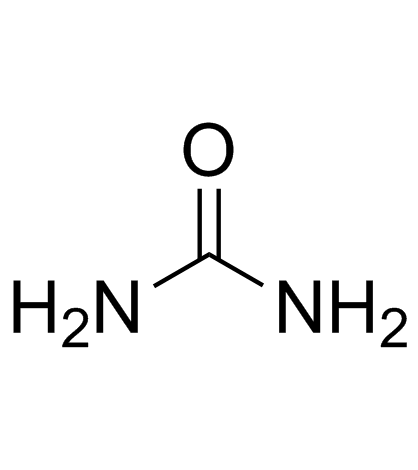 |
Urea
CAS:57-13-6 |
|
 |
Sodium deoxycholate
CAS:302-95-4 |
|
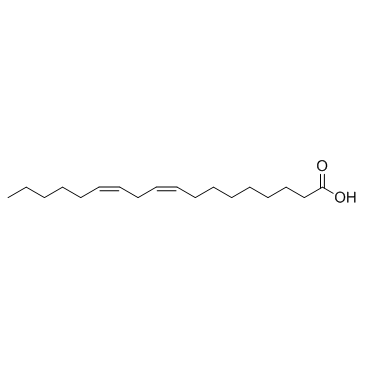 |
Linoleic acid
CAS:60-33-3 |
|
 |
DL-Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
CAS:591-59-3 |
|
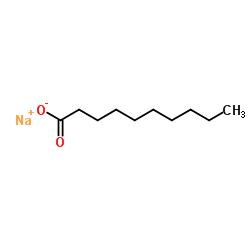 |
Sodium decanoate
CAS:1002-62-6 |
|
 |
UNII:TF4710DNP9
CAS:5094-24-6 |