| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Piroxicam
CAS:36322-90-4 |
|
 |
L-Nicotine
CAS:54-11-5 |
|
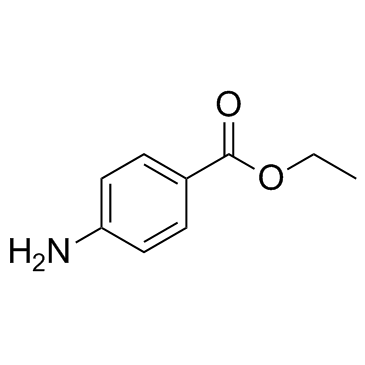 |
Benzocaine
CAS:94-09-7 |
|
 |
Mebendazole
CAS:31431-39-7 |
|
 |
Caffeine
CAS:58-08-2 |
|
 |
Hydrocortisone
CAS:50-23-7 |
|
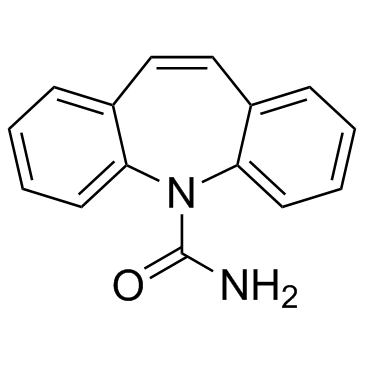 |
Carbamazepine
CAS:298-46-4 |
|
 |
Lidocaine
CAS:137-58-6 |
|
 |
Corticosterone
CAS:50-22-6 |
|
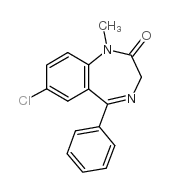 |
diazepam
CAS:439-14-5 |