| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine
CAS:150-25-4 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
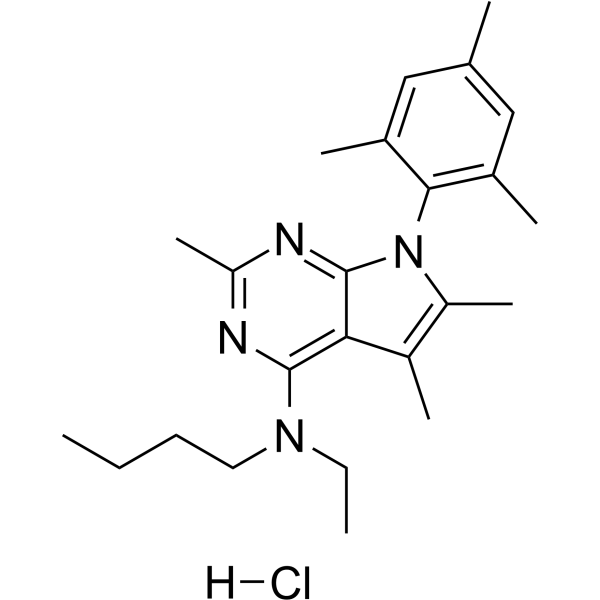 |
Antalarmin hydrochloride
CAS:220953-69-5 |