| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
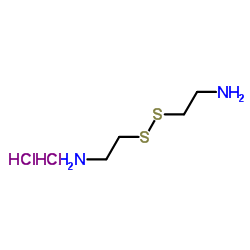 |
Cystamine dihydrochloride
CAS:56-17-7 |
|
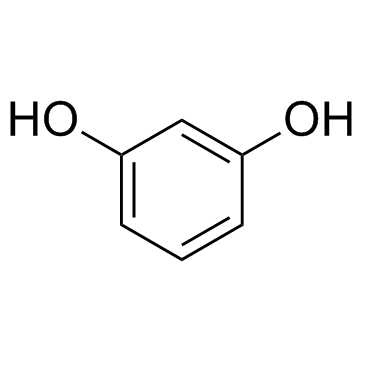 |
Resorcine
CAS:108-46-3 |
|
 |
Salicylic acid
CAS:69-72-7 |
|
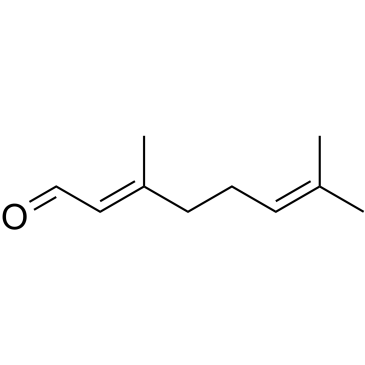 |
Citral
CAS:5392-40-5 |
|
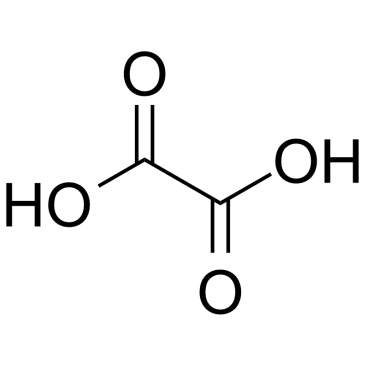 |
Oxalic acid
CAS:144-62-7 |
|
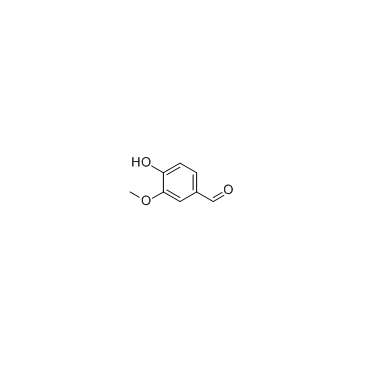 |
Vanillin
CAS:121-33-5 |
|
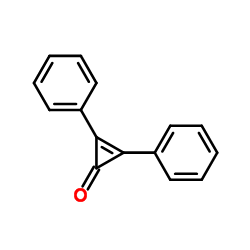 |
DPC
CAS:886-38-4 |
|
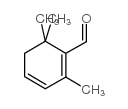 |
SAFRANAL
CAS:116-26-7 |
|
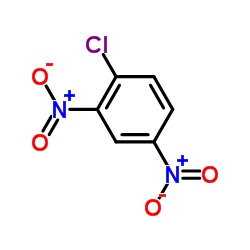 |
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
CAS:97-00-7 |
|
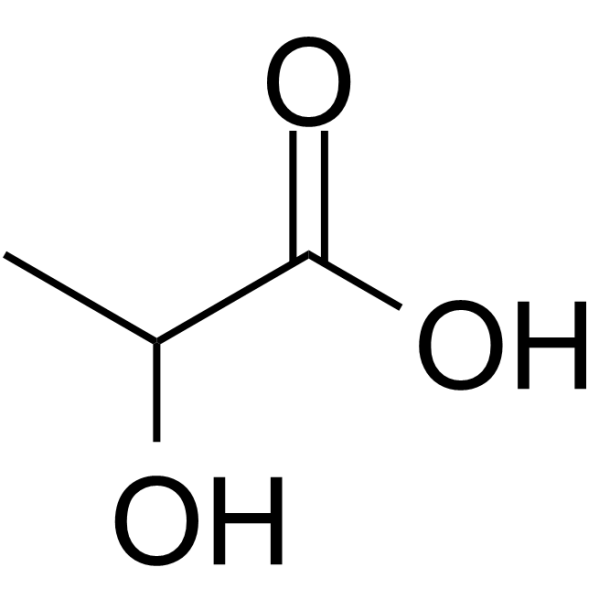 |
Lactic acid
CAS:50-21-5 |