Vanillin
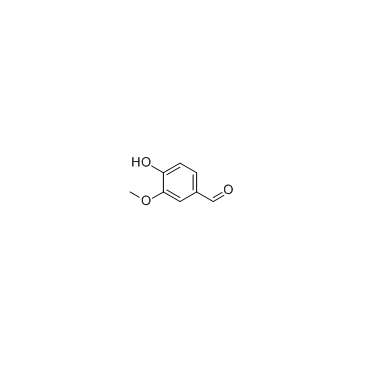
Vanillin structure
|
Common Name | Vanillin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 121-33-5 | Molecular Weight | 152.147 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 282.6±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O3 | Melting Point | 81-83 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 117.6±15.3 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of VanillinVanillin is a single molecule extracted from vanilla beans and also a popular odor used widely in perfume, food and medicine. |
| Name | vanillin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Vanillin is a single molecule extracted from vanilla beans and also a popular odor used widely in perfume, food and medicine. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| In Vitro | Vanillin recovers UVA-induced reduction of proliferation in a dose dependent manner. Vanillin has no apoptotic effects at the tested concentrations. In addition, the reduced expression levels of OCT4, NANOG, and SOX2 caused by UVA irradiation are allincreased by Vanillin treatment, suggesting that Vanillin attenuates the effects of UVA irradiation on hAMSCs. Based on a luciferase reporter assay, Vanillin increases the reduced activity of HRE-luciferase reporter caused by UVA irradiation. In addition, treatment with Vanillin attenuates the reduced expression of HIF-1α caused by UVA irradiation. The results reveal that treatment of hAMSCs with Vanillin results in significant decrease in the production of PGE2 and cAMP when compare to UVA-irradiated controls[1]. |
| In Vivo | Following antidepressant treatment for 4 weeks, immobility time in the stress+Vanillin and stress+fluoxetine groups is significantly decreased [F(4,42)=34.73, P<0.01; F(4,42)=13.55, P<0.01, respectively]. Treatment with Vanillin or fluoxetine remarkably alleviates the decrease in sucrose consumption in CUMS model animals [F(4,42)=12.32, P<0.01; F(4,42)=5.65, P<0.01, respectively]. In CUMS model rats, 5-HT level in the stress+Vanillin and stress+fluoxetine groups is significantly increased when compare with the stress group [F(4,42)=4.846, P=0.030; F(4,42)=4.846, P=0.036, respectively], whereas noradrenaline (NE) in the two groups is elevated but not significantly [F(4,42)=6.977, n.s.]. Dopamine (DA) is also significantly increased in the stress+Vanillin group compare with the stress group [F(4.42)=6.174, P=0.041][2]. |
| Kinase Assay | hAMSCs are irradiated with the indicated doses of UVA and then incubated with the indicated concentrations of Vanillin for three days under serum-free conditions. After the incubation, the concentrations of PGE2 or cAMP in the culture supernatant are measured using ELISA kits. Culture supernatants are added into 96 well plates. Alkaline phosphatase conjugated PGE2 or cAMP and antibodies to PGE2 or cAMP are added to sample wells and incubated at room temperature for 2 h. The sample wells are then washed with PBS and p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNpp) substrate solution is added. Finally, the samples are incubated at room temperature for 1 h and their absorbance values are read according to the manufacturer's instructions[1]. |
| Cell Assay | hAMSCs are irradiated with the indicated doses of UVA and then incubated with 1 to 100 μM of Vanillin for three days under serum-free conditions (in DMEM devoid of serum, at 37°C with 5% CO2). After three days, cell proliferation is measured using BrdU incorporation assay[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Male Sprague-Dawley rats (200 to 250 g) are used in this study. The animals are divided into three groups with 8 to 10 rats per group: the stress+fluoxetine group; the stress+Vanillin aromatherapy group and the stress (untreated) group. For the stress+fluoxetine group, the animals are administered a daily oral dose (10 mg/kg/d, diluted in distilled water) of the SSRI fluoxetine each morning. For the stress+Vanillin group and the bulbectomy+Vanillin group, Vanillin is administrated in a Plexiglas cylinder 50 cm tall and 35 cm diameter with two layers separated by a porous Plexiglas board. The rat still in its cage is gently placed on the upper layer, and 5 mL of 600 mg/L Vanillin (in distilled water) sprayed on to the floor of the lower layer. Rats in the stress and the control groups receive similar handling to the stress+Vanillin group, but without any odor administrated[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 282.6±20.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 81-83 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H8O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 152.147 |
| Flash Point | 117.6±15.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 152.047348 |
| PSA | 46.53000 |
| LogP | 1.19 |
| Vapour density | 5.3 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.588 |
| Storage condition | Refrigerator |
| Stability | Stable. May discolour on exposure to light. Moisture-sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, perchloric acid. |
| Water Solubility | 10 g/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H319 |
| Precautionary Statements | P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R22 |
| Safety Phrases | S24/25-S22 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | YW5775000 |
| HS Code | 2912410000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2912410000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | HS: 2912410000. 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde. VAT:17.0%. tax rebate rate:13.0%. supervision conditions:None. MFN tarrif:5.5%. general tariff:30.0% |
|
Antimicrobial activity of natural products from the flora of Northern Ontario, Canada.
Pharm. Biol. 53(6) , 800-6, (2015) The number of multidrug resistant (MDR) microorganisms is increasing and the antimicrobial resistance expressed by these pathogens is generating a rising global health crisis. In fact, there are only ... |
|
|
Detoxification of biomass hydrolysates with nucleophilic amino acids enhances alcoholic fermentation.
Bioresour. Technol. 186 , 106-13, (2015) Carbonyl compounds generated in biomass pretreatment hinder the biochemical conversion of biomass hydrolysates to biofuels. A novel approach of detoxifying hydrolysates with amino acids for ethanol pr... |
|
|
Effect of selected Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains and different aging techniques on the polysaccharide and polyphenolic composition and sensorial characteristics of Cabernet Sauvignon red wines.
J. Sci. Food Agric. 95 , 2132-44, (2015) The objective of this work was to study the effect of two Saccharomyces cerevisiae yeast strains with different capabilities of polysaccharide liberation during alcoholic fermentation in addition to s... |
| 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde,Vanillic aldehyde |
| Lioxin |
| 3-Methoxy-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde |
| Vanillin (contains H2SO4) Ethanol |
| VANILLA |
| VANILLINE |
| Zimco |
| 4-oxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde |
| Reference source: Negwer |
| Vinillin |
| compound no 1131 |
| Rhovanil |
| 3-methoxy-4-hydroxy-benzaldehyde |
| Vanilin |
| Vanillin |
| MFCD00006942 |
| 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde |
| EINECS 204-465-2 |
| FEMA 3107 |
 CAS#:120-14-9
CAS#:120-14-9 CAS#:93-51-6
CAS#:93-51-6![4-[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/266/69404-94-0.png) CAS#:69404-94-0
CAS#:69404-94-0 CAS#:5932-68-3
CAS#:5932-68-3![3-methoxy-4-[(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy]benzaldehyde Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/022/91471-08-8.png) CAS#:91471-08-8
CAS#:91471-08-8 CAS#:67-56-1
CAS#:67-56-1 CAS#:498-00-0
CAS#:498-00-0 CAS#:5533-00-6
CAS#:5533-00-6 CAS#:97-54-1
CAS#:97-54-1![2-(2-chloroindolo[2,3-b]quinoxalin-6-yl)-N'-[(Z)-(3-methoxy-4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)methyl]acetohydrazide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/274/109322-03-4.png) CAS#:109322-03-4
CAS#:109322-03-4![(E)-2-cyano-3-[4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-5-(phenylsulfanylmethyl)phenyl]prop-2-enamide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/258/107788-00-1.png) CAS#:107788-00-1
CAS#:107788-00-1![N'-[(Z)-(3-methoxy-4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)methyl]-2-[4-[(Z)-(3-methyl-5-oxo-1H-pyrazol-4-ylidene)methyl]phenoxy]acetohydrazide structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/359/107044-96-2.png) CAS#:107044-96-2
CAS#:107044-96-2 CAS#:106174-97-4
CAS#:106174-97-4 CAS#:104202-36-0
CAS#:104202-36-0 CAS#:110642-42-7
CAS#:110642-42-7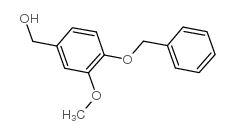 CAS#:33693-48-0
CAS#:33693-48-0 CAS#:52783-83-2
CAS#:52783-83-2 CAS#:32024-15-0
CAS#:32024-15-0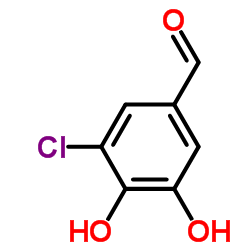 CAS#:34098-18-5
CAS#:34098-18-5
