Kinetic studies on a novel sulfotransferase from Eubacterium A-44, a human intestinal bacterium.
D H Kim, K Kobashi
Index: J. Biochem. 109(1) , 45-8, (1991)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
A novel sulfotransferase purified from a human intestinal bacterium stoichiometrically catalyzed the transfer of a sulfate group of phenylsulfate esters to phenolic compounds. Vmax values of the enzyme reaction were measured with various concentrations of a sulfate donor substrate, p-nitrophenylsulfate, and of a sulfate acceptor substrate, tyramine. Double reciprocal plots of the acceptor concentration and Vmax showed a linear correlation. One of the reaction products, tyramine O-sulfate, competitively inhibited the enzyme as to a donor substrate, p-nitrophenylsulfate (PNS), but the other reaction product, p-nitrophenol (PNP), noncompetitively inhibited it as to PNS. These kinetic data suggest that the sulfate transfer reaction proceeds according to a ping pong bi bi mechanism. The enzyme was activated by Mg2+ and inhibited by EDTA, which suggests that it is a metalloenzyme.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
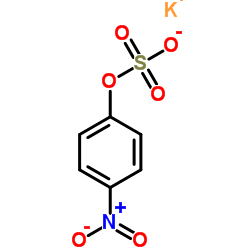 |
Potassium 4-nitrophenyl sulfate
CAS:6217-68-1 |
C6H4KNO6S |
|
Relationship between substrate activity and pKa value of phe...
1992-12-01 [Biochem. Int. 28(4) , 725-34, (1992)] |
|
Regulation of arylsulfate sulfotransferase from a human inte...
1995-01-01 [J. Enzym. Inhib. 8(4) , 233-41, (1995)] |
|
Sulfating-activity and stability of cDNA-expressed allozymes...
1999-08-01 [J. Biochem. 126(2) , 271-7, (1999)] |
|
para-Nitrophenyl sulfate activation of human sulfotransferas...
2009-10-23 [J. Biol. Chem. 284(43) , 29357-64, (2009)] |
|
Natural killer cell cytolytic granule-associated enzymes. I....
1991-08-01 [J. Immunol. 147(3) , 950-8, (1991)] |