| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
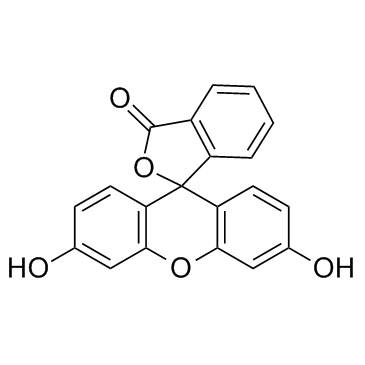 |
Fluorescein
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
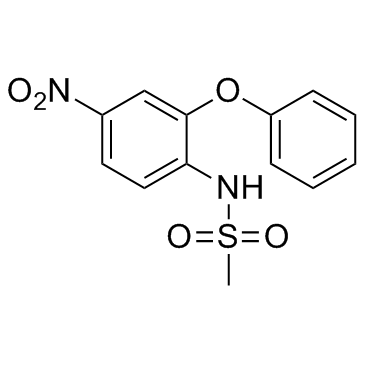 |
Nimesulide
CAS:51803-78-2 |
|
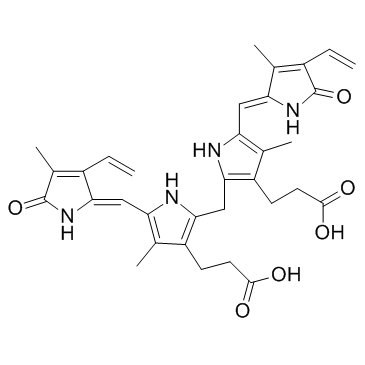 |
bilirubin
CAS:635-65-4 |
|
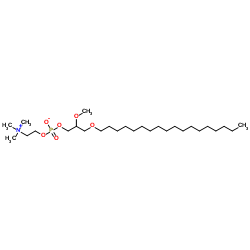 |
Edelfosine
CAS:70641-51-9 |