| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
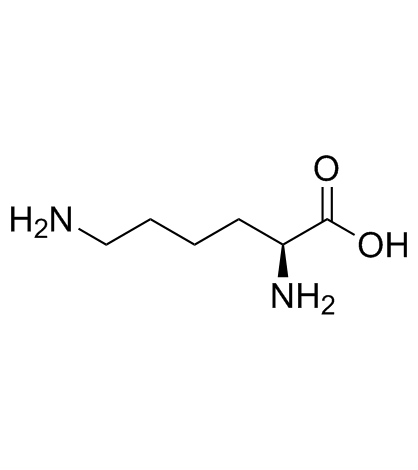 |
L-Lysine
CAS:56-87-1 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
 |
Histone, from calf thymus
CAS:9064-47-5 |
|
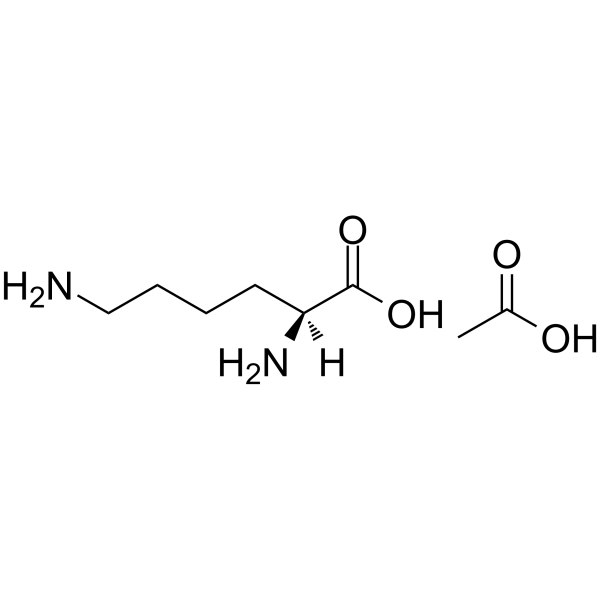 |
L-Lysine monoacetate
CAS:57282-49-2 |