| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
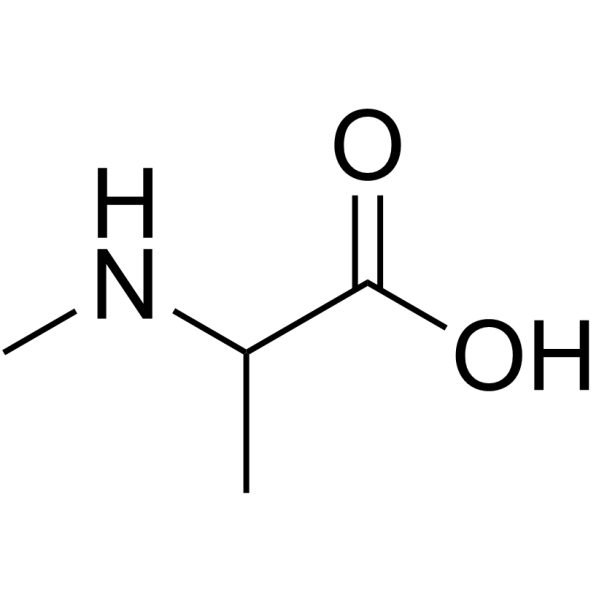 |
N-Me-DL-Ala-OH.HCl
CAS:600-21-5 |
|
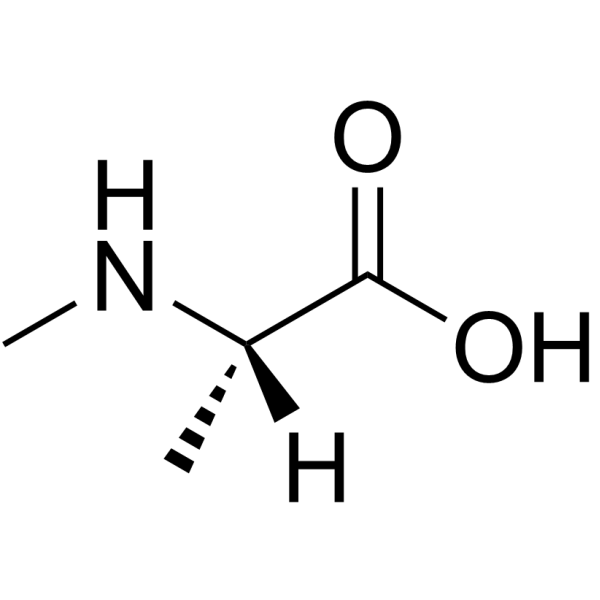 |
H-N-Me-Ala-OH.HCl
CAS:3913-67-5 |