| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
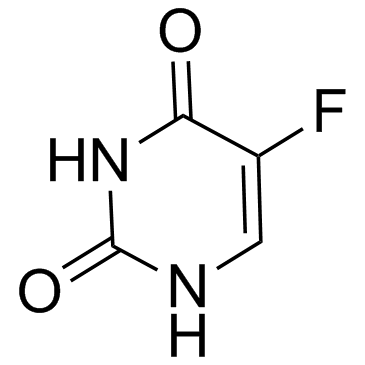 |
Fluorouracil
CAS:51-21-8 |
|
 |
Broxuridine
CAS:59-14-3 |
|
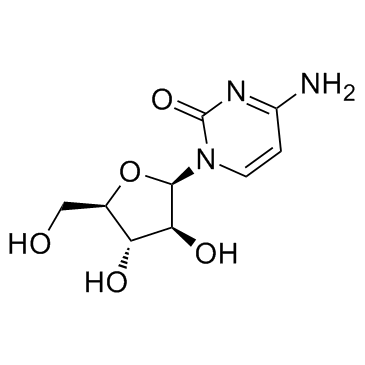 |
Cytarabine
CAS:147-94-4 |
|
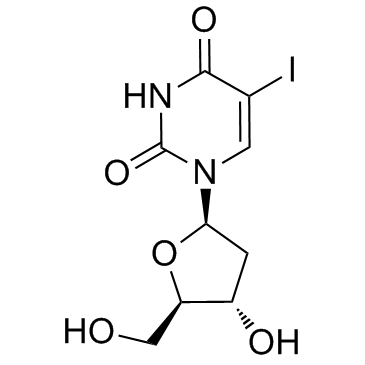 |
idoxuridine
CAS:54-42-2 |