| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
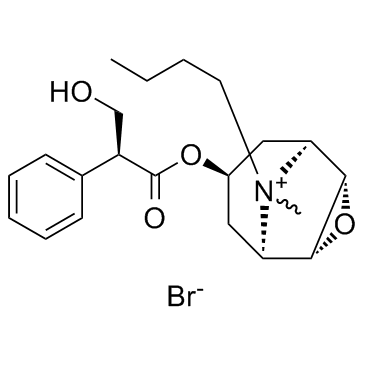 |
Scopolamine butylbromide
CAS:149-64-4 |
|
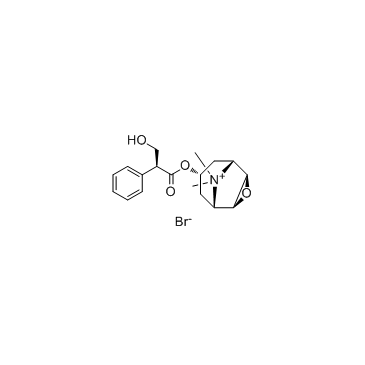 |
Methscopolamine (bromide)
CAS:155-41-9 |
|
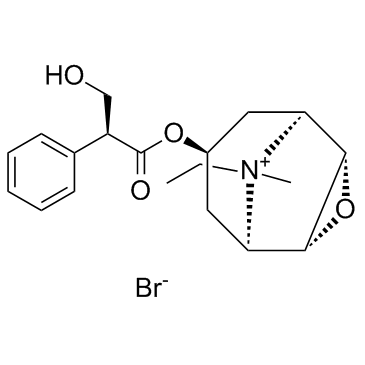 |
Oxitropium Bromide
CAS:30286-75-0 |