| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide
CAS:7529-22-8 |
|
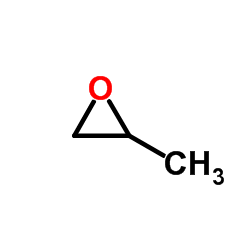 |
epoxypropane
CAS:75-56-9 |
|
 |
DL-Propargylglycine
CAS:64165-64-6 |
|
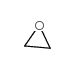 |
ETHYLENE OXIDE
CAS:75-21-8 |
|
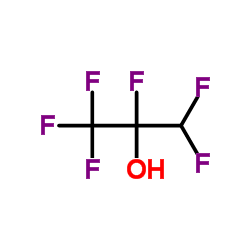 |
Hexafluoroisopropanol
CAS:920-66-1 |
|
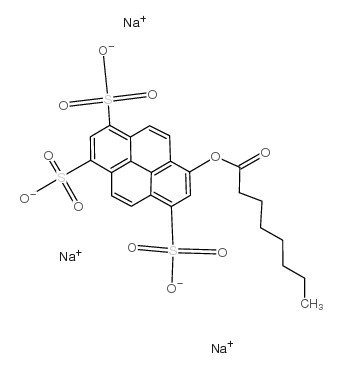 |
8-Octanoyloxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium salt
CAS:115787-84-3 |