| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
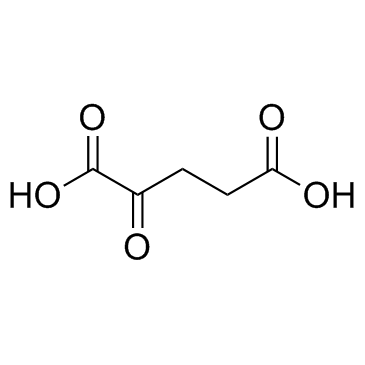 |
2-Ketoglutaric acid
CAS:328-50-7 |
|
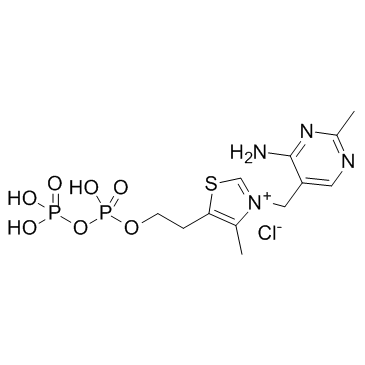 |
Cocarboxylase
CAS:154-87-0 |
|
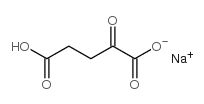 |
Alpha-Ketoglutaric acid sodium salt
CAS:22202-68-2 |
|
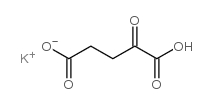 |
Potassium hydrogen 2-oxoglutarate
CAS:997-43-3 |
|
 |
Pyruvate Oxidase
CAS:9001-96-1 |