| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
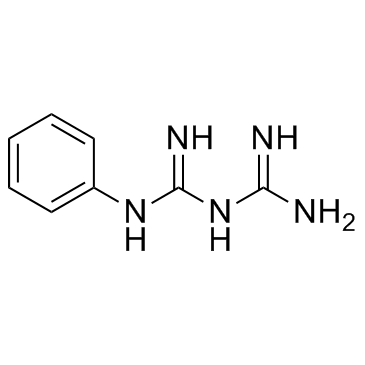 |
Phenylbiguanide
CAS:102-02-3 |
|
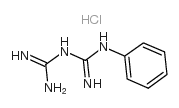 |
1-phenylbiguanide hydrochloride
CAS:55-57-2 |
|
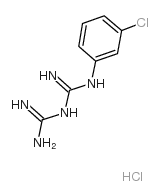 |
1-(3-chlorophenyl)biguanide hydrochloride
CAS:2113-05-5 |