| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
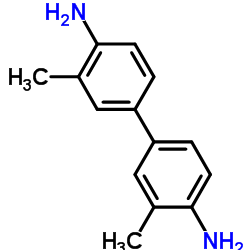 |
3,3'-dimethylbenzidine
CAS:119-93-7 |
|
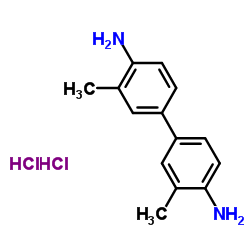 |
4,4'-Bi-o-toluidine dihydrochloride
CAS:612-82-8 |