| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
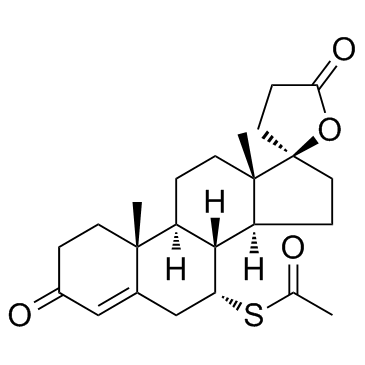 |
Spironolactone
CAS:52-01-7 |
|
 |
Finasteride
CAS:98319-26-7 |
|
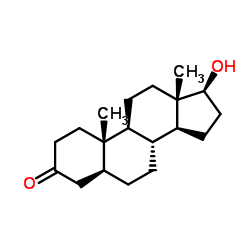 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
 |
D-AMPHETAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE
CAS:51-64-9 |