| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Phentolamine hydrochloride
CAS:73-05-2 |
|
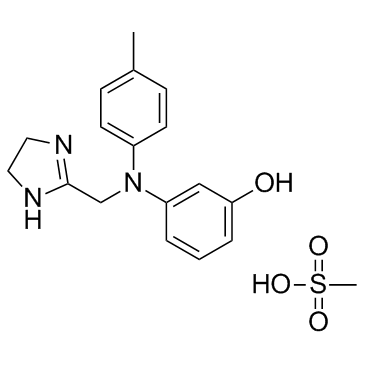 |
Phentolamine mesilate
CAS:65-28-1 |
|
 |
Bretylium (tosylate)
CAS:61-75-6 |