| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
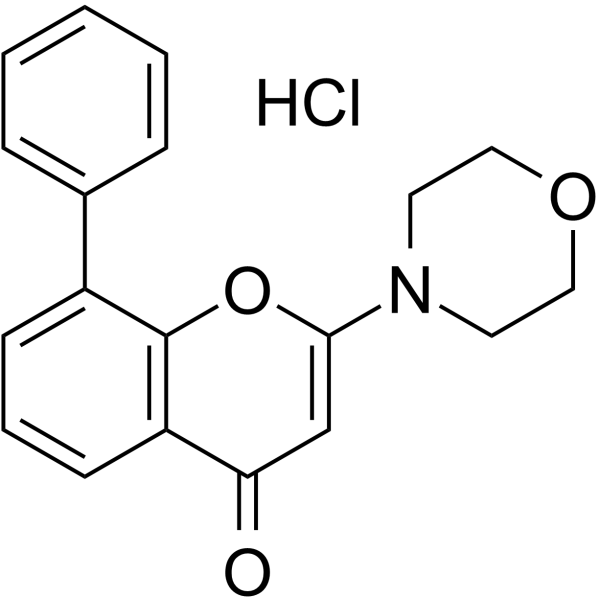 |
LY-294,002 hydrochloride
CAS:934389-88-5 |
|
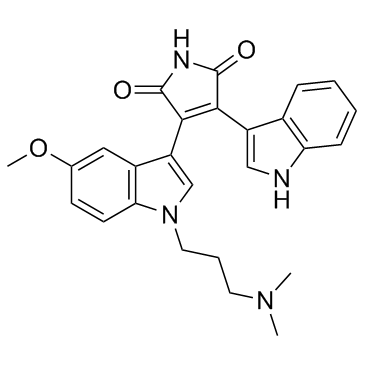 |
Go 6983
CAS:133053-19-7 |