Specificity and efficacy of noradrenaline, serotonin depletion in discrete brain areas of Swiss mice by neurotoxins.
Eric Dailly, Franck Chenu, Benoit Petit-Demoulière, Michel Bourin
Index: J. Neurosci. Methods 150(1) , 111-5, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The aim of this work is to define neurotoxins doses to have efficient and specific depletion of noradrenaline (NA), serotonin (5-HT) neurotransmission in cortex, striatum, hippocampus and hypothalamus of Swiss mice after intraperitoneal administration of, respectively, N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-ethyl-2-bromobenzylamine hydrochloride (DSP-4) and para-chlorophenylalanine methyl ester hydrochloride (PCPA). The neurotransmitters concentrations were determined by high performance liquid chromatography with amperometric detection. The minimal single dose necessary to produce a highly significant decrease of NA levels (p<0.01 in comparison with control group) in hypothalamus (-44%), hippocampus (-91%), striatum (-40%) and cortex (-68%) was 50mg/kg but DA and 5-HT levels were modified, respectively, in hypothalamus and striatum. Three doses of PCPA 300 mg/kg over 3 consecutive days involve a profound depletion of 5-HT transmission in all discrete brain areas but NA and DA levels were also significantly reduced. In conclusion, DSP-4 has a different efficacy in discrete brain areas with a noradrenergic specificity which is not absolute, PCPA has a similar efficacy in all brain areas but is unspecific of 5-HT transmission.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
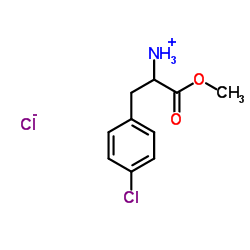 |
PCPA methyl ester hydrochloride
CAS:14173-40-1 |
C10H13Cl2NO2 |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state ...
2007-05-01 [Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007)] |
|
A test to determine the nature and presence of the memory ef...
2011-09-16 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1218(37) , 6302-7, (2011)] |
|
AMPA glutamate receptors mediate the antidepressant-like eff...
2012-04-01 [Behav. Pharmacol. 23(2) , 171-7, (2012)] |
|
Ankle joint mobilization affects postoperative pain through ...
2013-03-01 [Phys. Ther. 93(3) , 401-12, (2013)] |
|
Inhibition of hypothalamic nitric oxide synthase gene expres...
1995-11-01 [J. Neuroendocrinol. 7(11) , 861-5, (1995)] |