The accumulation and disposition of benz(a)acridine in the fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas.
G R Southworth, C C Keffer, J J Beauchamp
Index: Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 10(5) , 561-9, (1981)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The bioconcentration and metabolism of benz(a)acridine in fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) was investigated using 14C-labelled benz(a)acridine. The rates of uptake, elimination, and metabolic transformation of benz(a)acridine were estimated in the fish. The equilibrium concentration factor [ratio of benz(a)acridine concentration in fish (wet weight) to benz(a)acridine concentration in water] was estimated at 106 +/- 17. The observed bioconcentration factor was about one tenth of that predicted by octanol-water partitioning models. Metabolic alteration was estimated to reduce the degree of bioconcentration 50 to 90% from the hypothetical case in which metabolic transformation did not occur. Benz(a)acridine metabolites attained concentrations in the fish considerably in excess of benz(a)acridine itself.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
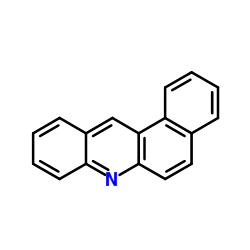 |
benz(a)acridine
CAS:225-11-6 |
C17H11N |
|
Substituted benz[a]acridines and benz[c]acridines as mammali...
2000-05-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8(5) , 1171-82, (2000)] |
|
Benz[a]acridine.
1983-12-01 [IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risk Chem. Hum. 32 , 123-7, (1983)] |
|
Mutagenicity of diol-epoxides and tetrahydroepoxides of benz...
1983-04-01 [Cancer Res. 43(4) , 1656-62, (1983)] |
|
On the metabolic activation of benz[a]acridine and benz[c]ac...
1982-09-01 [Cancer Lett. 16(3) , 297-306, (1982)] |
|
Experimental studies on the carcinogenicity of five nitrogen...
1983-08-01 [Cancer Lett. 20(1) , 97-101, (1983)] |