| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ampicillin
CAS:69-53-4 |
|
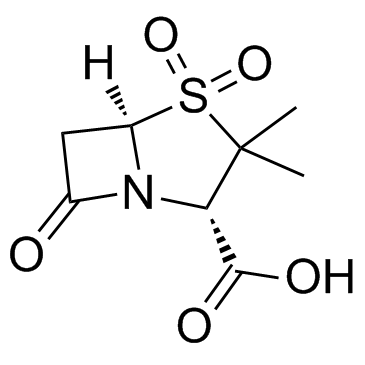 |
Sulbactam
CAS:68373-14-8 |
|
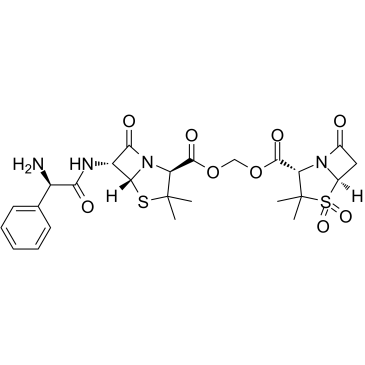 |
Sultamicillin
CAS:76497-13-7 |