Escherichia coli peptidase A, B, or N can process translation inhibitor microcin C.
Teymur Kazakov, Gaston H Vondenhoff, Kirill A Datsenko, Maria Novikova, Anastasia Metlitskaya, Barry L Wanner, Konstantin Severinov
Index: J. Bacteriol. 190(7) , 2607-10, (2008)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The heptapeptide-nucleotide microcin C (McC) targets aspartyl-tRNA synthetase. Upon its entry into a susceptible cell, McC is processed to release a nonhydrolyzable aspartyl-adenylate that inhibits aspartyl-tRNA synthetase, leading to the cessation of translation and cell growth. Here, we surveyed Escherichia coli cells with singly, doubly, and triply disrupted broad-specificity peptidase genes to show that any of three nonspecific oligopeptidases (PepA, PepB, or PepN) can effectively process McC. We also show that the rate-limiting step of McC processing in vitro is deformylation of the first methionine residue of McC.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
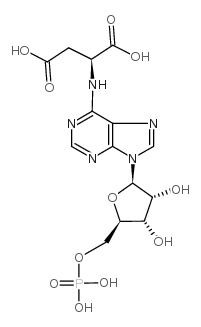 |
Adenylosuccinic acid
CAS:19046-78-7 |
C14H18N5O11P |
|
The RimL transacetylase provides resistance to translation i...
2014-10-01 [J. Bacteriol. 196(19) , 3377-85, (2014)] |
|
Synthesis and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitory activity ...
2005-01-03 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13(1) , 69-75, (2005)] |
|
MccE provides resistance to protein synthesis inhibitor micr...
2010-04-23 [J. Biol. Chem. 285(17) , 12662-9, (2010)] |
|
[Aspartyladenylate analog--effective inhibitor of asparagine...
1988-07-01 [Bioorg. Khim. 14(7) , 969-72, (1988)] |
|
Aspartyl tRNA-synthetase from Escherichia coli: flexibility ...
2000-06-23 [J. Mol. Biol. 299(5) , 1157-64, (2000)] |