Purification and characterization of mycobacterial phospholipase A: an activity associated with mycobacterial cutinase.
Sarah K Parker, Kathryn M Curtin, Michael L Vasil
Index: J. Bacteriol. 189(11) , 4153-60, (2007)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
We describe mycobacterial phospholipase A activity (MPLA) and, using reverse genetics, have associated this activity with putative mycobacterial cutinase. PLAs, which hydrolyze fatty acids on phospholipids, play a significant role in human inflammatory states and disease pathogenesis. In prokaryotes, the recognition of their role in virulence is more recent. Cutinases are serine esterases whose primary substrate is cutin, the waxy exterior layer of plants. Mycobacterium tuberculosis has maintained seven putative cutinases, though it should not encounter cutin; we demonstrate that known cutinases and MPLA cleave phospholipids in a PLA-type manner and also hydrolyze Tween. We analyzed cutinase motifs in mycobacteria and found the motif very prevalent. All mycobacteria tested had MPLA activity. These studies suggest an alternative use for putative cutinases by the M. tuberculosis group that is likely related to MPLA activity and lipid metabolism.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
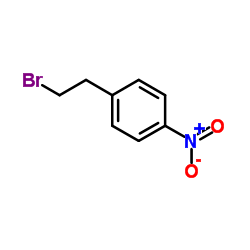 |
1-(2-Bromoethyl)-4-nitrobenzene
CAS:5339-26-4 |
C8H8BrNO2 |
|
An ensemble of theta class glutathione transferases with nov...
2002-04-19 [J. Mol. Biol. 318(1) , 59-70, (2002)] |
|
Residue 234 in glutathione transferase T1-1 plays a pivotal ...
2005-05-15 [Biochem. J. 388(Pt 1) , 387-92, (2005)] |
|
A glutathione S-transferase (GST) isozyme from broccoli with...
1994-03-16 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1205(1) , 29-38, (1994)] |
|
Kinetic characterization of recombinant human glutathione tr...
1997-12-15 [Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 348(2) , 247-54, (1997)] |
|
Enzymatic inactivation of major circulating forms of atrial ...
1999-04-16 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 370(3) , 307-12, (1999)] |