Doxercalciferol

Doxercalciferol structure
|
Common Name | Doxercalciferol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 54573-75-0 | Molecular Weight | 412.648 | |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 538.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H44O2 | Melting Point | 138-140ºC | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 224.0±24.7 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
Use of DoxercalciferolDoxercalciferol is a Vitamin D2 analog, acts as an activator of Vitamin D receptor, and prevent renal disease. |
| Name | 1α-Hydroxy Vitamin D2 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Doxercalciferol is a Vitamin D2 analog, acts as an activator of Vitamin D receptor, and prevent renal disease. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Vitamin D receptor[1] |
| In Vivo | Doxercalciferol (0.083, 0.167 or 0.333 μg/kg, i.p.) elevates serum phosphorus at Week 6 in 5/6 nephrectomized (NX) rats. Doxercalciferol (0.167 and 0.333 μg/kg) also increases serum calcium and Ca × P at Weeks 2 and 6, and enhances increased pulse wave velocity (PWV) at Week 6 in 5/6 nephrectomized (NX) rats. Doxercalciferol blocks PTH from rising at 0.083 μg/kg, and lowers serum PTH to the SHAM level[1]. Doxercalciferol (125 ng/kg, i.p. thrice per week) increases expression of VDR mRNA level and renal expression of TRPV5 in NON mice fed a HF diet. Doxercalciferol also improves proteinuria, prevents loss of podocytes, and accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins in HF diet-induced mice. Doxercalciferol inhibits the expression of profibrotic growth factors (TGF-β, PAI-1, and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF)), and blocks increased expression of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in mice fed a HF diet. Furthermore, Doxercalciferol suppresses macrophage infiltration, decreases NF-κb activity, and preventes expression of proinflammatory cytokine and the increase in renal lipid accumulation in mice fed a HF diet[2]. Doxercalciferol (30 ng/kg, i.p. thrice per week) prevents albuminuria, markedly attenuates podocyte loss and apoptosis, and reduces glomerular fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[1] Male, Sprague-Dawley, 5/6 nephrectomized (NX) rats (∼200 gm) are used 1 week after nephrectomy. The nephrectomy is performed using a standard two-step surgical ablation procedure. Beginning 2 weeks post-nephrectomy, rats are maintained on a high phosphorus diet (0.9% phosphorus and 0.6% calcium) for the duration of the study to induce secondary hyperparathyroidism. On Day 0, SHAM and 5/6 NX rats (n = 7-10 per group) receive vehicle (5% EtOH/95% propylene glycol; 0.4 mL/kg; i.p.) or VDRA (paricalcitol or Doxercalciferol; 0.083, 0.167 or 0.333 μg/kg; intraperitoneally) three times per week for 41 days (n = 6-10 per group). These doses are chosen based on the fact that lower doses (0.021 and 0.042 μg/kg; i.p.) of either compound are not PTH suppressive after 2 or 6 weeks of treatment in this model of CKD. On Days 0, 13 and 41, blood is collected (24 h post-dose). On Days 0, 13 and 41 (24 h post-dose), animals are anaesthetized with ketamine (50 mg/kg) and blood is collected via the tail vein for PTH and serum blood chemistry determinations[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 538.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 138-140ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C28H44O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 412.648 |
| Flash Point | 224.0±24.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 412.334137 |
| PSA | 40.46000 |
| LogP | 8.15 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.541 |
| InChIKey | HKXBNHCUPKIYDM-XXZMWSRPSA-N |
| SMILES | C=C1C(=CC=C2CCCC3(C)C2CCC3C(C)C=CC(C)C(C)C)CC(O)CC1O |
| Storage condition | Desiccate at -20°C |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H300 |
| Precautionary Statements | P264-P301 + P310 |
| Hazard Codes | T+ |
| Risk Phrases | 28 |
| Safety Phrases | 28-36/37-45 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1 / PGIII |
|
~% 
Doxercalciferol CAS#:54573-75-0 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 51, # 9 p. 1635 - 1637 |
|
~% 
Doxercalciferol CAS#:54573-75-0 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 51, # 9 p. 1635 - 1637 |
|
~% 
Doxercalciferol CAS#:54573-75-0 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 51, # 9 p. 1635 - 1637 |
|
~% 
Doxercalciferol CAS#:54573-75-0 |
| Literature: Journal of Organic Chemistry, , vol. 51, # 9 p. 1635 - 1637 |
|
Calcium regulates FGF-23 expression in bone.
Endocrinology 154(12) , 4469-82, (2013) Calcium has recently been shown to regulate fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23), a bone-derived phosphate and vitamin D-regulating hormone. To better understand the regulation of FGF-23 by calcium, p... |
|
|
Recent changes in therapeutic approaches and association with outcomes among patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism on chronic hemodialysis: the DOPPS study.
Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10(1) , 98-109, (2015) Elevated parathyroid hormone levels may be associated with adverse clinical outcomes in patients on dialysis. After the introduction of practice guidelines suggesting higher parathyroid hormone target... |
|
|
A new look at the most successful prodrugs for active vitamin D (D hormone): alfacalcidol and doxercalciferol.
Molecules 14(10) , 3869-80, (2009) Alfacalcidol (1alpha-hydroxyvitamin D(3)) has been widely used since 1981 as a prodrug for calcitriol (1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)) in the treatment of hypocalcemia, chronic renal failure, hypopar... |
| UNII-3DIZ9LF5Y9 |
| (1S,3R,5Z,7E,22E)-9,10-Secoergosta-5,7,10,22-tetraene-1,3-diol |
| doxercalciferol |
| MFCD01076571 |
| (1R,3S,5Z)-4-methylidene-5-[(2E)-2-{(1R,3aS,7aR)-7a-methyl-1-[(1R,2E,4R)-1,4,5-trimethylhex-2-en-1-yl]octahydro-4H-inden-4-ylidene}ethylidene]cyclohexane-1,3-diol |
| Hectorol |
![(1S,3E,5R)-3-[(2E)-2-[(1R,3aS,7aR)-1-[(E,2R,5R)-5,6-dimethylhept-3-en-2-yl]-7a-methyl-2,3,3a,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-inden-4-ylidene]ethylidene]-5-[tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl]oxy-2-methylidenecyclohexan-1-ol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/483/112670-78-7.png)
![tert-Butyl-dimethyl-(4-methylene-3-{2-[7a-methyl-1-(1,4,5-trimethyl-hex-2-enyl)-octahydro-inden-4-ylidene]-ethylidene}-cyclohexyloxy)-silane structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/327/104846-62-0.png)
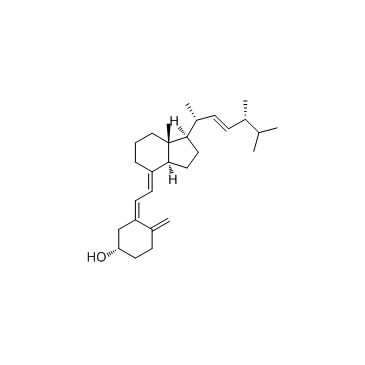
![3-[7a-Methyl-1-(1,4,5-trimethyl-hex-2-enyl)-octahydro-inden-4-ylidenemethyl]-2,2-dioxo-2,3,4,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-2l6-benzo[c]thiophen-5-ol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/302/87407-73-6.png)