119509-24-9
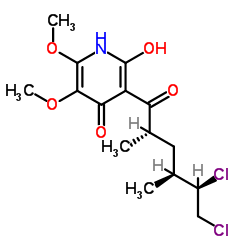
| Name | 3-[(2S,4S,5R)-5,6-dichloro-2,4-dimethylhexanoyl]-4-hydroxy-5,6-dimethoxy-1H-pyridin-2-one |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
3-[(2S,4S,5R)-5,6-Dichloro-2,4-dimethylhexanoyl]-2-hydroxy-5,6-dimethoxy-4(1H)-pyridinone
AT5 3-[(2S,4S,5R)-5,6-DICHLORO-2,4-DIMETHYL-1-OXOHEXYL]-4-HYDROXY-5,6-DIMETHOXY-2(1H)-PYRIDINONE Atpenin A5 |
| Description | Atpenin A5 is a potent and highly specific complex II inhibitor (IC50 ~10 nM), and is an effective mKATP channel agonist and cardioprotective agent[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Atpenin A5 shows the inhibition profile for submitochondrial particles (SMPs), mitochondria, and cardiomyocytes, with IC50 values of 8.3, 9.3, and 8.5 nM, respectively. Atpenin A5 (AA5) is a potent and specific complex II inhibitor. Atpenin A5 (1 nM) also activates the mKATP channel and protects against simulated ischemia-reperfusion (IR) injury in isolated cardiomyocytes[1]. |
| In Vivo | Atpenin A5 is a potent inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase (SDH). Succinate dehydrogenase inhibition by Atpenin A5 promotes cardiomyocyte mitosis and regeneration in the postnatal heart after myocardial infarction (MI). Atpenin A5-injected mice demonstrated myocardial thickness at the infarct zone and a significant reduction in scar size compared with controls[2]. Animal Model: Neonatal mice[2] Dosage: 100 μg/kg Administration: Injected daily Result: Demonstrated myocardial thickness at the infarct zone and a significant reduction in scar size compared with controls. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 532.6±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C15H21Cl2NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 366.237 |
| Flash Point | 275.9±30.1 °C |
| Exact Mass | 365.079681 |
| PSA | 88.62000 |
| LogP | -0.80 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.534 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|