153832-46-3
| Name | ertapenem |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
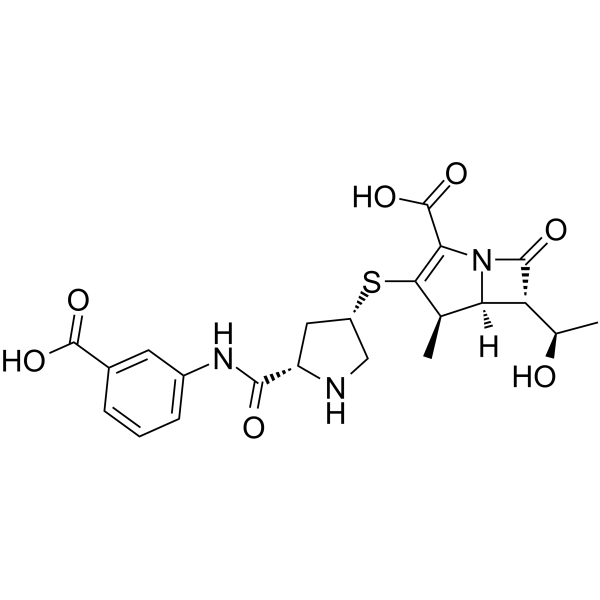
(4R,5S,6S)-3-({(3S,5S)-5-[(3-Carboxyphenyl)carbamoyl]-3-pyrrolidinyl}sulfanyl)-6-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid
ertapenem [INN_en] (4R,5S,6S)-3-({(3S,5S)-5-[(3-Carboxyphenyl)carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl}sulfanyl)-6-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (4R,5S,6S)-3-[(3S,5S)-5-[(3-carboxyphenyl)carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-3-yl]sulfanyl-6-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-4-methyl-7-oxo-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]hept-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid Ertapenem AC-6814 UNII-G32F6EID2H |
| Description | Ertapenem (MK-0826) is a broad spectrum and long acting β-lactam antibiotic. Ertapenem has a broad-spectrum anti-anaerobic activity against a variety of anaerobes with a mode MIC of 0.12 μg/mL. Ertapenem can be used for the research of severe infections caused by bacteria in the skin, lungs, stomach, pelvis, and urinary tract[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Ertapenem (0-100 μg/mL approximately, 48 h) is active against 99.1% of all anaerobes with a mode MIC of 0.12 μg/mL and MIC90 of 1 μg/mL, and MIC’s ≥8 μg/mL for B.fragilis and B.vulgatus species, respectively[1]. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Line: B. fragilis (ATCC 25285), B. thetaiotaomicron (ATCC 29741), and Eubacterium lentum (ATCC 43055) Concentration: 0-100 μg/mL approximately Incubation Time: 48 h Result: Inhibited 99.1% of all isolate with a mode MIC of 0.12 μg/mL and MIC90 of 1 μg/mL, and 98.8% of the isolates were susceptible among the B. fragilis group. |
| In Vivo | Ertapenem (Subcutaneous injection, 0-10 mg/kg, 0-120 h after infection, S. aureus thigh tissue infection model) shows > 3 log10 CFU reduction of organism at 10 mg/kg, and maintains the activity with 3.3 and 4.4 log10 CFU eliminated at 2 mg/kg[2]. Ertapenem (Subcutaneous injection, 4h after infection, systemic infection model) is active against all gram-positive organisms, and is also active against gram-negative organisms tested with ED50s of <0.25 mg/kg/dose[2]. Animal Model: S. aureus thigh tissue infection model (DBA/2 mice)[2] Dosage: 0.5,1, 2, 5, 10 mg/kg (given at 2, 6, 10, 24, 48, 72, 96, 120 h) Administration: Subcutaneous injection (0.5 mL after infection) Result: Displayed > 3 log10 CFU reduction of organism compared to non-antibiotic-treated controls at 10 mg/kg. Maintained the activity with 3.3 and 4.4 log10 CFU eliminated at 2 mg/kg. Animal Model: Systemic infection model (DBA/2 female mice, viral antibody-free CD-1 female mice)[2] Dosage: 0-3 mg/kg approximately Administration: Subcutaneous injection (0.5 mL, begin immediately and 4 h after infection) Result: Showed activity against all gram-positive organisms, and also ram-negative organisms tested with ED50s of <0.25 mg/kg/dose. Animal Model: CD-1 mice, rats[2] Dosage: 10 mg/kg approximately Administration: Intraperitoneal injection (pharmacokinetic assay) Result: Exhibited an AUC0-∞ ranging from 1.8-21.82 μg•hr/mL in tissue in mice following a 10-mg/kg i.p. dose. Exhibited slow clearance rate with a t1/2β of 3.2 h, Clp of 0.47 mL/min/kg, AUC0-8 of 284.15μg•hr/mL. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 813.9±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C22H25N3O7S |
| Molecular Weight | 475.515 |
| Flash Point | 446.0±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 475.141327 |
| PSA | 181.57000 |
| LogP | -1.07 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.700 |