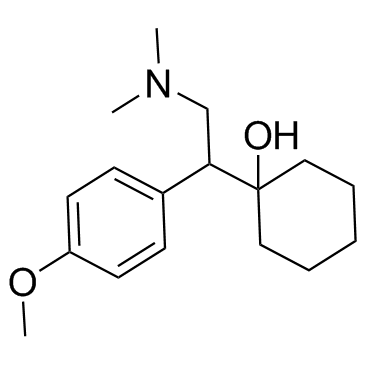
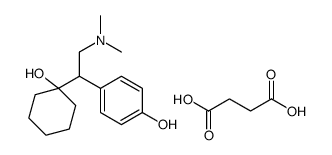
99300-78-4
| Name | venlafaxine hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1-[2-(Dimethylamino)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]cyclohexanol hydrochloride (1:1)
Efectin Venlafaxine Hydrochloride Effexor Venlafaxine HCl MFCD03658865 EINECS 200-659-6 Cyclohexanol, 1-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-, hydrochloride (1:1) Efexor (±)-1-(a-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-p-methoxybenzyl)cyclohexanol hydrochloride cyclohexanol, 1-[2-(dimethylamino)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-, hydrochloride RTECS GV8872760 |
| Description | Venlafaxine hydrochloride is an antidepressant of the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class.Target: SNRIVenlafaxine is an antidepressant of the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class. First introduced by Wyeth in 1993, now marketed by Pfizer, it is licensed for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), as a treatment for generalized anxiety disorder, and comorbid indications in certain anxiety disorders with depression. In 2007, venlafaxine was the sixth most commonly prescribed antidepressant on the U.S. retail market, with 17.2 million prescriptions.Venlafaxine is a bicyclic antidepressant, and usually categorized as a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), but it has been referred to as a serotonin-norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI). It works by blocking the transporter "reuptake" proteins for key neurotransmitters affecting mood, thereby leaving more active neurotransmitters in the synapse. The neurotransmitters affected are serotonin and norepinephrine. Additionally, in high doses it weakly inhibits the reuptake of dopamine, with recent evidence showing that the norepinephrine transporter also transports some dopamine as well, since dopamine is inactivated by norepinephrine reuptake in the frontal cortex. The frontal cortex largely lacks dopamine transporters; therefore, venlafaxine can increase dopamine neurotransmission in this part of the brain. Venlafaxine interacts with opioid receptors (mu-, kappa1- kappa3- and delta-opioid receptor subtypes) as well as the alpha2-adrenergic receptor, and was shown to increase pain threshold in mice. When mice were tested with a hotplate analgesia meter (to measure pain), both venlafaxine and mirtazapine induced a dose-dependent, naloxone-reversible antinociceptive effect following intraperitoneal injection. These findings suggest venlafaxine's seemingly superior efficacy in severe depression as narcotics become increasingly used as a measure of last resort for refractory cases. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.394 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 397.6ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 207-209ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C17H28ClNO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 313.863 |
| Flash Point | 194.2ºC |
| Exact Mass | 313.180847 |
| PSA | 32.70000 |
| LogP | 3.83760 |
| Storage condition | Store at RT |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS02, GHS06, GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H225-H301 + H311 + H331-H370 |
| Precautionary Statements | P210-P260-P280-P301 + P310-P311 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xi: Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | 26-37/39 |
| RIDADR | 1230.0 |
| RTECS | GV8872760 |
| Hazard Class | 3、6.1 |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|
~96% 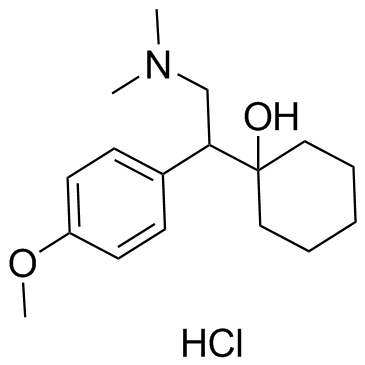
99300-78-4 |
| Literature: AARTI HEALTHCARE LIMITED Patent: WO2007/69277 A2, 2007 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 12-15 ; |
|
~95% 
99300-78-4 |
| Literature: Siegfried Ltd. Patent: EP2072495 A1, 2009 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 9 ; |
|
~% 
99300-78-4 |
| Literature: US2010/94055 A1, ; Page/Page column 4-5 ; |
|
~% 
99300-78-4 |
| Literature: EP1721889 A1, ; Page/Page column 6 ; |
|
~78% 
99300-78-4 |
| Literature: TEVA PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LTD.; TEVA PHARMACEUTICALS USA, INC. Patent: WO2007/47972 A2, 2007 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 16; 17 ; |
|
~% 
99300-78-4 |
| Literature: WO2007/49302 A2, ; Page/Page column 7-8 ; |
|
~% 
99300-78-4 |
| Literature: Organic Process Research and Development, , vol. 15, # 6 p. 1392 - 1395 |
|
~% 
99300-78-4 |
| Literature: Organic Process Research and Development, , vol. 15, # 6 p. 1392 - 1395 |
|
~% 
99300-78-4 |
| Literature: Organic Process Research and Development, , vol. 15, # 6 p. 1392 - 1395 |
| Precursor 8 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 3 | |
| HS Code | 2922509090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2922509090. other amino-alcohol-phenols, amino-acid-phenols and other amino-compounds with oxygen function. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:30.0% |