29767-20-2
| Name | teniposide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
etp
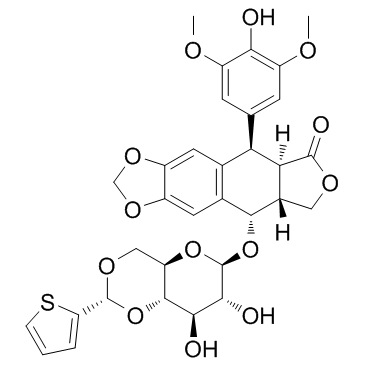
Pipodophyllotoxin VM 26 Teniposide/VM-26 vm-26 (5S,5aR,8aR,9R)-9-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-8-oxo-5,5a,6,8,8a,9-hexahydrofuro[3',4':6,7]naphtho[2,3-d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl 4,6-O-(2-thienylmethylene)-β-D-glucopyranoside vehem Teniposide Teniposide(VuMon) EINECS 249-831-2 MFCD00866516 Vumon |
| Description | Teniposide is a podophyllotoxin derivative, acts as a topoisomerase II inhibitor, and used as a chemotherapeutic agent. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Topoisomerase II |
| In Vitro | Teniposide is a topoisomerase II inhibitor. Teniposide (VM-26, 0.15-45 mg/L) inhibits the proliferation of Tca8113 cells in a dose-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 0.35 mg/L. Teniposide (5 mg/L) induces apoptosis of Tca8113 cells. Teniposide (5.0 mg/L) causes cell arrested at G2/M phase in Tca8113 cells[2]. Teniposide is active on primary cultured glioma cells from patients, when the level of miR-181b is high in the cells, with an IC50 of 1.3 ± 0.34 μg/mL. Cells treated with teniposide with low MDM2 have decreased viability compared with control cells, and the IC50 decreases from 5.86 ± 0.36 μg/mL to 2.90 ± 0.35 μg/mL upon MDM2 suppression. Teniposide also inhibits the viability of glioma cell with high level of miR-181b, through mediation of MDM2[3]. |
| In Vivo | Teniposide (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly increases micronucleated polychromatic erythrocyte (MNPCE) frequencies, which is directly related to bone marrow toxicity as significant suppression of bone marrow is noted. Teniposide (24 mg/kg, i.p.) markedly decreases the frequencies of BrdU-labelled sperm. Teniposide (12, 24 mg/kg, i.p.) also dramatically induces disomic sperm in the germ cell of male mice[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Logarithmically growing Tca8113 cells are trypsinized and made into single cell suspension then plated in 96-well culture plate at a concentration of 5 × 104 cells/well, eight columns for Teniposide and seven columns for CDDP in each plate, 3 wells in each column. After 24 hours of incubation, the medium of the 3 wells in each column are replaced with medium containing Teniposide of 0.15 mg/L, 0.5 mg/L, 1.5 mg/L, 5.0 mg/L, 15 mg/L and 45 mg/L or CDDP of 0.1 mg/L, 0.3 mg/L, 1.0 mg/L, 3.0 mg/L and 9.0 mg/L, respectively. Blank control wells are added medium without drugs. Cells are then cultured for another 24 hours, 48 hours, 72 hours, 96 hours and 120 hours. The supernatants are removed and 20 μL MTT solution is added in each well, followed with another 4 hours of culture. The supernatants are discarded carefully and 200 μL dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) is added and shaken vigorously to dissolve the purple precipitation formation. Optical density (OD) of each well is tested using Spectrophotometer with a wavelength of 450 nm. The experiment is repeated in triplicate[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Animals (mice) are treated with 0.5 mg/kg teniposide and bone marrow is sampled 24 h after treatment. Colchicine and mitomycin C are used as a positive control aneugen and clastogen, respectively, at the dose of 2 mg/kg each. Bone marrow smears are prepared and stained with May-Gruenwald/Giemsa solutions. At least four slides are made for each animal and allowed to dry overnight. One slide per animal is stained with May-Gruenwald/Giemsa solutions for conventional assessment of the micronuclei (MN) frequencies in polychromatic erythrocytes (PCEs) and normochromatic erythrocytes (NCEs). The remaining unstained slides are stored at −20°C for the distinction between the clastogenic and aneugenic effects by identifying the origin of MN with the mouse DNA probes. Per animal, 1000 PCE of coded slides are scored for the presence of MN. In addition, the number of PCEs among 1000 NCE per animal is recorded to evaluate bone marrow suppression and mitotic activity is calculated as %PCE = [PCE/(PCE + NCE)] × 100[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 864.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 274 - 277ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C32H32O13S |
| Molecular Weight | 656.654 |
| Flash Point | 476.5±34.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 656.156372 |
| PSA | 189.07000 |
| LogP | 1.71 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.697 |
| Storage condition | -20°C Freezer |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
MUTATION DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS08 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H350 |
| Precautionary Statements | P201-P308 + P313 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S36 |
| RIDADR | 3276 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | KC0180000 |