868049-49-4
| Name | olodaterol |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
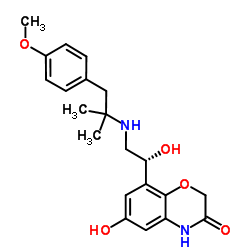
6-Hydroxy-8-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-{[1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-methyl-2-propanyl]amino}ethyl]-2H-1,4-benzoxazin-3(4H)-one
Striverdi Respimat BI 1744 6-hydroxy-8-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-[[1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropan-2-yl]amino]ethyl]-4H-1,4-benzoxazin-3-one UNII-VD2YSN1AFD Olodaterol |
| Description | Olodaterol (BI1744) is a selective, long acting β2-adrenoceptor (β2-AR) agonist (EC50=0.1 nM and pKi= 9.14 for human β2-adrenoceptor, respectively). Olodaterol can be used for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and pulmonary fibrosis[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
β2 adrenoceptor:0.1 nM (EC50) |
| In Vitro | Olodaterol (0.001~10 nM; fibroblasts) attenuates growth factor-induced motility and proliferation[2]. Olodaterol (0.1~10 nM; fibroblasts) interferes with FGF-induced phosphorylation of signalling cascades[2]. Olodaterol (0.001~1000 nM; 30 minutes; fibroblasts) increases intracellular cAMP in a concentration-dependent manner. Olodaterol (0~10 nM; 30 minutes; fibroblasts) concentration-dependently inhibits the PICP increase with maximal efficacy of 70 % at 10 nM. Olodaterol has a subnanomolar affinity for the β2-AR (pKi=9.14) and is selective for this receptorin comparison with the β1-AR and β3-AR subtypes[2]. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Line: Fibroblasts Concentration: 0.1~10 nM Incubation Time: Result: Interfered with FGF-induced phosphorylation of signalling cascades. Cell Proliferation Assay[2] Cell Line: Fibroblasts Concentration: 0.001~10 nM Incubation Time: Result: Attenuated growth factor-induced motility and proliferation. |
| In Vivo | Olodaterol (1 mg/kg; inhal.; 21 days) accelerats body weight recovery back to control levels (at day 21) and attenuats TGF-β-induced lung fibrosis[2]. Olodaterol (0.1~3 μg/kg; inhal.; 5 hours) induces a dose-dependent bronchoprotection[3]. Olodaterol (0.3 and 0.6 μg/kg; inhal.; 24 hours) induces a maximal bronchoprotection of approximately 60 % after 0.5 hours[3]. Animal Model: Lung fibrosis C57BL/6 mice Dosage: 1 mg/mL Administration: Inhal.; 21 days Result: Accelerated body weight recovery back to control levels (at day 21) and attenuated TGF-β-induced lung fibrosis. Animal Model: Guinea Pigs Dosage: 0.1~3 μg/kg Administration: Inhal.; 5 hours Result: Induced a dose-dependent bronchoprotection. Animal Model: Dogs Dosage: 0.3 and 0.6 μg/kg Administration: Inhal.; 24 hours Result: Olodaterol (0.6 μg/kg) induced a maximal bronchoprotection of approximately 60 % after 0.5 hours. |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 649.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C21H26N2O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 386.441 |
| Flash Point | 346.3±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 386.184174 |
| PSA | 103.54000 |
| LogP | 1.17 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.596 |
|
~% 
868049-49-4 |
| Literature: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH Patent: US2005/267106 A1, 2005 ; Location in patent: Page/Page column 8 ; |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |