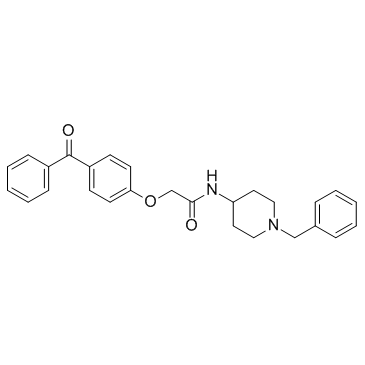
924416-43-3
| Name | Acetamide, 2-(4-benzoylphenoxy)-N-[1-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl] |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-(4-Benzoylphenoxy)-N-(1-benzyl-4-piperidinyl)acetamide
AdipoRon SC-396658 |
| Description | AdipoRon is an orally active adiponectin receptor (AdipoR) agonist, binding to AdipoR1 and AdipoR2 with Kds of 1.8 and 3.1 μM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Kd: 1.8 μM (AdipoR1), 3.1 μM (AdipoR2)[1] |
| In Vitro | AdipoRon is an orally active and specific AdipoR agonist, binds to AdipoR1 and AdipoR2, with Kds of 1.8 and 3.1 μM. AdipoRon (50 nM-50 μM) increases AMPK phosphorylation via AdipoR1[1]. AdipoRon (50 μM) dose-dependently attenuates the expression of TNF-α and TGF-β1 in the L02 cells. AdipoRon exhibits significant and dosage-dependent growth suppression on macrophages[2]. AdipoRon treatment significantly improves cardiac functional recovery after reperfusion, and inhibits post-MI apoptosis[3]. AdipoRon exerts vasodilation by mechanisms distinct to adiponectin and induces vasorelaxation without a marked decrease in VSMC [Ca2+]i[4]. |
| In Vivo | AdipoRon (50 mg/kg, i.v.) cuases significant phosphorylation of AMPK in skeletal muscle and liver of wild-type mice but not Adipor1−/− Adipor2−/− double-knockout mice[1]. AdipoRon (0.02, 0.1, and 0.5 mg/kg, i.g.) alleviates D-GalN induced hepatotoxicity in mice, and prevents hepatic architecture distortion against D-GalN challenge. The hepatoprotective potential of AdipoRon is particularly evident in higher dosages (0.1 and 0.5 mg/kg)[2]. Enhanced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in APN-deficient mice is rescued by AdipoRon (50 mg/kg, p.o.) administration. Antiapoptotic effect of AdipoRon is attenuated but not lost in AMPK-DN mice[3]. |
| Cell Assay | The effects of AdipoRon on the proliferation of parenchymal and non-parenchymal hepatocytes are evaluated in vitro via L02 and RAW264.7, by MTT assay as described with slight modification: 100 μL cells suspension (6×104/mL) are seeded in a 96-well plate and incubated for 18 h. Fresh media with AdipoRon are added at specified concentrations, and the incubations continue for a further 24 h. Then cells are incubated for 4 h with 0.5 mg/mL of MTT, and analyzed in a microplate reader at 490 nm. Each group is performed in six replications. The mean absorbance values corrected for a blank (medium only) are calculated as percentages of survival[2]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice[2] After 3 days of acclimation, mice are randomLy divided into six groups (9 mice in each): control, model, bicyclol (20 mg/kg), AdipoRon (0.02 mg/kg, 0.1 mg/kg, 0.5 mg/kg). The synthetic AdipoRon and bicyclol are dissolved in DMSO and diluted by saline containing 0.5% sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC-Na) [final vehicle: 5% DMSO (v/v) saline solution]. All test groups are administered with vehicle (control and model groups) or therapeutic agents (bicyclol or AdipoRon groups) at a dosing volume of 10 mL/kg, by intragastric (i.g.) gavage twice per day for three consecutive days prior to D-GalN administration. 2 h after last treatment, mice are challenged with a single intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of D-GalN saline solution at a dose of 600 mg/kg to induce acute liver injury, while the control group mice receive saline instead. Then mice are fasted for 20 h before orbital blood collection. Finally, all animals are sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and livers are harvested for biochemical or histopathology analysis[2]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 645.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C27H28N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 428.523 |
| Flash Point | 344.1±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 428.209991 |
| PSA | 58.64000 |
| LogP | 4.14 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.632 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Symbol |


GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P501 |
| RIDADR | UN 3077 9 / PGIII |