842133-18-0
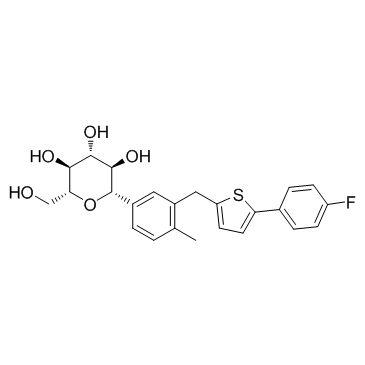
| Name | Canagliflozin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MFCD18251436
Canagliflozin purity JNJ 28431754 UNII-6S49DGR869 Canagliflozin anhydrous Canagliflozin canagliflozin (*) (1S)-1,5-Anhydro-1-(3-{[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-thienyl]methyl}-4-methylphenyl)-D-glucitol (2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-(3-((5-(4-fluorophenyl)thiophen-2-yl)methyl)-4-methylphenyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol TA 7284 (1S)-1,5-Anhydro-1-C-[3-[[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-thienyl]methyl]-4-methylphenyl]-D-glucitol |
| Description | Canagliflozin is a selective SGLT2 inhibitor with IC50s of 2 nM, 3.7 nM, and 4.4 nM for mSGLT2, rSGLT2, and hSGLT2 in CHOK cells, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 2/3.7/4.4 nM (m/r/hSGLT2, in CHOK cells)[1] |
| In Vitro | Canagliflozin is a sodium glucose co-transporter (SGLT) 2 inhibitor. In a concentration-dependent fashion, Canagliflozin inhibits Na+-dependent 14C-AMG uptake in CHO-hSGLT2 cells, with an IC50 of 4.4±1.2 nM. Similar IC50 values are obtained in CHO-rSGLT2 and CHO-mSGLT2 cells (IC50=3.7 and 2.0 nM for rat and mouse SGLT2, respectively). Canagliflozin inhibits 14C-AMG uptake in CHO-hSGLT1 and mSGLT1 cells with IC50 of 684±159 nM and >1,000 nM, respectively. At 10 µM, Canagliflozin inhibits the facilitative (non-Na+-linked) GLUT-mediated 3H-2-DG uptake in L6 myoblasts by less than 50%[1]. |
| In Vivo | Canagliflozin treatment (1 mg/kg) notably lowers renal threshold for glucose excretion (RTG) in Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats to 94±10 mg/dL. In the second study, an insulin infusion is given to lower blood glucose (BG) to approximately 25 mg/dL, and then the graded glucose infusion (GGI) is given to slowly raise BG to approximately 300 mg/dL. In ZDF rats treated with Canagliflozin (1 mg/kg), the relationship between BG and urinary glucose excretion (UGE) remains well-described by a threshold relationship with negligible UGE occurring when BG<90 mg/dL and UGE increases in proportion to BG at higher BG levels. In db/db mice, single doses of Canagliflozin dose-dependently reduces non-fasting BG concentrations. The onset of the BG-lowering effect after a single dose is rapid, and BG levels in Canagliflozin-treated mice (at 1 and 10 mg/kg doses) are significantly different from those of vehicle-treated mice at 1 hour after treatment (22% and 36% reduction of BG levels compared with that in vehicle-treated mice, respectively)[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Sodium-dependent glucose uptake in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells expressing SGLT1 and SGLT2 co-transporters parental CHO-K (CHOK) cells (commonly used mammalian cells for gene overexpression studies) expressing human or mouse SGLT1 and SGLT2 are utilized in this study. Cells are seeded into 96-well plates. Cells are then washed one time with 0.15 mL assay buffer (137 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, 1 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.4) at 37°C. After the assay buffer is removed, 50 µL of fresh assay buffer with 5 µL of Canagliflozin (0.3-300 nM) is added, followed by 10 minutes of incubation. Then, 5 µL of 6 mM alpha-methyl-D-glucopyranoside (AMG, a selective SGLT1/2 substrate)/14C-AMG (0.07 µCi) is added to the cells and incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. Next, the cells are washed 3 times with 0.15 mL ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). After the final wash is aspirated, 50 µL of microscint 20 is added. The plate is counted by TopCount[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice and Rats[1] Four rodent models are used in these experiments: (1) male C57BL/6J mice fed with a high-fat diet (D-12492 with 60 kcal% fat) (diet-induced obese, insulin resistantmice [DIO]); (2) male C57BL/ksj-db/db hyperglycemic mice; (3) male Zucker fatty (ZF) obese, insulin resistant rats; and (4) male ZDF obese, hyperglycemic rats. To examine the effect of Canagliflozin on hyperglycemia, single doses of Canagliflozin (0.1, 1, and 10 mg/kg) are administered to overnight-fasted db/db mice. BG levels are monitored at 0, 0.5, 1, 3, 6, and 24 hours after dosing. Canagliflozin is also administered to ZDF rats at varying doses (3-30 mg/kg) for 4 weeks to evaluate its effect on BG control and pancreatic beta-cell function. BG levels are monitored weekly, and HbA1c, plasma glucose, and insulin levels are determined at the end of the 4-week treatment. An oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) (2 mg/kg of body weight, given by gavage) is conducted in ZDF rats after 4 weeks of treatment. Blood is sampled at 0, 30, 60, and 120 minutes after glucose challenge from the tail vein for measurement of BG levels using a glucometer and plasma insulin using ELISA method. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 642.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C24H25FO5S |
| Molecular Weight | 444.516 |
| Flash Point | 342.6±31.5 °C |
| Exact Mass | 444.140686 |
| PSA | 118.39000 |
| LogP | 5.34 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.639 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
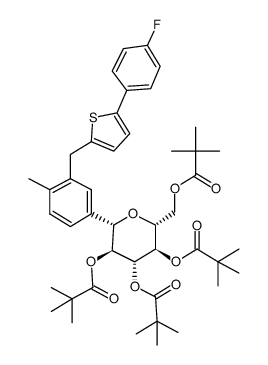
![(1S)-1,5-Anhydro-1-C-[3-[[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-thienyl]methyl]-4-methylphenyl]-D-glucitol tetraacetate structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/109/866607-35-4.png)
![Methyl 1-C-[3-[[5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-thienyl]methyl]-4-methylphenyl]-D-glucopyranoside structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/236/1030825-21-8.png)
![2-(4-Fluorophenyl)-5-[(5-iodo-2-Methylphenyl)methyl]thiophene structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/401/898566-17-1.png)